Scientists led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) designed a brand new PV-powered desalination system based mostly on time-variant electrodialysis reversal (EDR) expertise. The proposed system reportedly achieves a decrease water degree than typical solar-powered desalination tech.
A worldwide group of scientists led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has developed a novel low-cost solar-powered brackish water desalination system that may reportedly scale back the levelized value of water (LCOW) in comparison with typical PV-driven desalination programs.
The proposed desalination system makes use of time-variant electrodialysis reversal (EDR) expertise, which the researchers developed as a versatile variation of conventional EDR desalination. “Our analysis goals to handle water shortage in rural India the place many of the groundwater is just too salty to drink. Access and stability of electrical energy on the grid is poor, affected by frequent that energy reduce,” mentioned corresponding writer Wei He. pv journal.
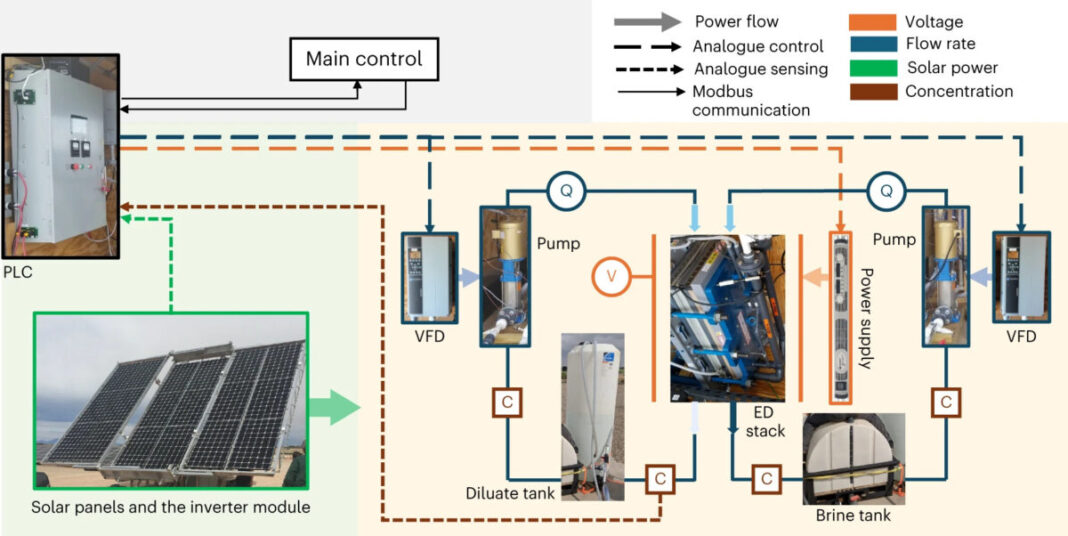
“An EDR module consists of a stack of ion alternate membranes and makes use of an electrical subject to switch ions from dilute stream channels to brine stream channels between every membrane,” mentioned the analysis group. “This electrical subject may be always reversed to forestall membrane scale build-up.”
However, as a result of fixed nature of photo voltaic vitality, the basic EDR just isn’t utterly appropriate. It requires fixed energy for its operation, and subsequently, PV-EDR vegetation want the help of batteries or redundant photo voltaic programs, particularly at first and finish of the day when the solar energy is low.
“To overcome these issues, we’ve got developed a versatile batch EDR expertise that features a time-variant voltage and stream charge adjustment,” the teachers defined. “A model-based management methodology permits the EDR system to adapt the ability consumption to the accessible solar energy at every time step whereas optimizing water manufacturing beneath totally different daytime circumstances.”
To management the operation, the group created a feed-forward, model-based predominant controller operating in Python to calculate the optimum pump stream charge and the EDR stack voltage based mostly on real-time sensor readings. A prototype was inbuilt a analysis facility, which intently displays the standard design parameters and working circumstances for a community-sized PV-EDR system to provide a 6 m3 tab. – the water day-after-day. It is powered by a photo voltaic panel with an space of 37 m2 and a tilt of 30 levels.
This pilot system was examined for one-day and six-day evaluation and in comparison with conventional steady operation EDR programs. Both programs had been fed by water with a median beginning salinity of 970 mg l−1. The system is about to a conservatively low water restoration ratio of 60%.
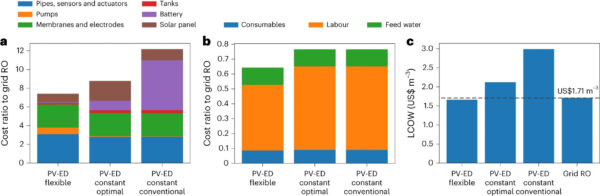
Image: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Nature Water, CC BY 4.0 DEED
“The versatile system is ready to instantly use 77% of the accessible photo voltaic vitality on common in comparison with solely 40% of the traditional system (a 91% enhance),” emphasised the scientists. “This suggests {that a} typical system would require extra photo voltaic panel space to function instantly (that’s, with none vitality storage), growing capital prices.”
In addition, the evaluation reveals that the common minimal battery capability required for the versatile system is 0.27 kWh, a 92% discount in comparison with the three.3 kWh of the fixed system. “Finally, the outcomes present that the versatile system can attain its manufacturing quantity as much as 54% quicker than the traditional system,” they added.
Following the outcomes of the experiment, the researchers performed a case research of the fee evaluation for using such a system in Chelluru, a village in rural India positioned close to Hyderabad. Using laptop simulation and optimization, it was in comparison with a traditional PV-EDR system, a state-of-the-art fixed PV-EDR, and a industrial on-grid reverse osmosis (RO) desalination system. “RO makes use of strain to power water via a polymer membrane, whereas its constitutive ions are blocked by the membrane,” the group mentioned.
“The optimized levelized value of water (LCOW) achieved by the proposed versatile PV-EDR system is US $1.66 m−3, which improves the fee by 22% in comparison with the present state-of-the-art PV -EDR system and by 46% in comparison with the traditional PV-EDR system,” the scientists discovered. “The LCOW for on-grid RO is US $1.71 m−3, 3% greater than the LCOW of versatile PV-EDR.”
Their findings are introduced in “Flexible batch electrodialysis for low-cost solar-powered brackish water desalination,” printed in Water in Nature. The group contains researchers from King’s College London within the UK, and Helmholtz Institute Erlangen-Nürnberg for Renewable Energy (HI ERN) in Germany.
“For the subsequent step, exploring the long-term efficiency and increasing the scope of utility of our PV-EDR expertise past brackish water desalination presents an necessary alternative to handle a larger variety of world challenges that associated to water and liquid waste remedy,” He concluded. .
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].