[ad_1]
In a brand new weekly replace for pv journalSolcast, a DNV firm, reviews that Australia skilled extreme and diversified climate all through July and August, leading to various results on photo voltaic irradiance throughout the nation’s states.
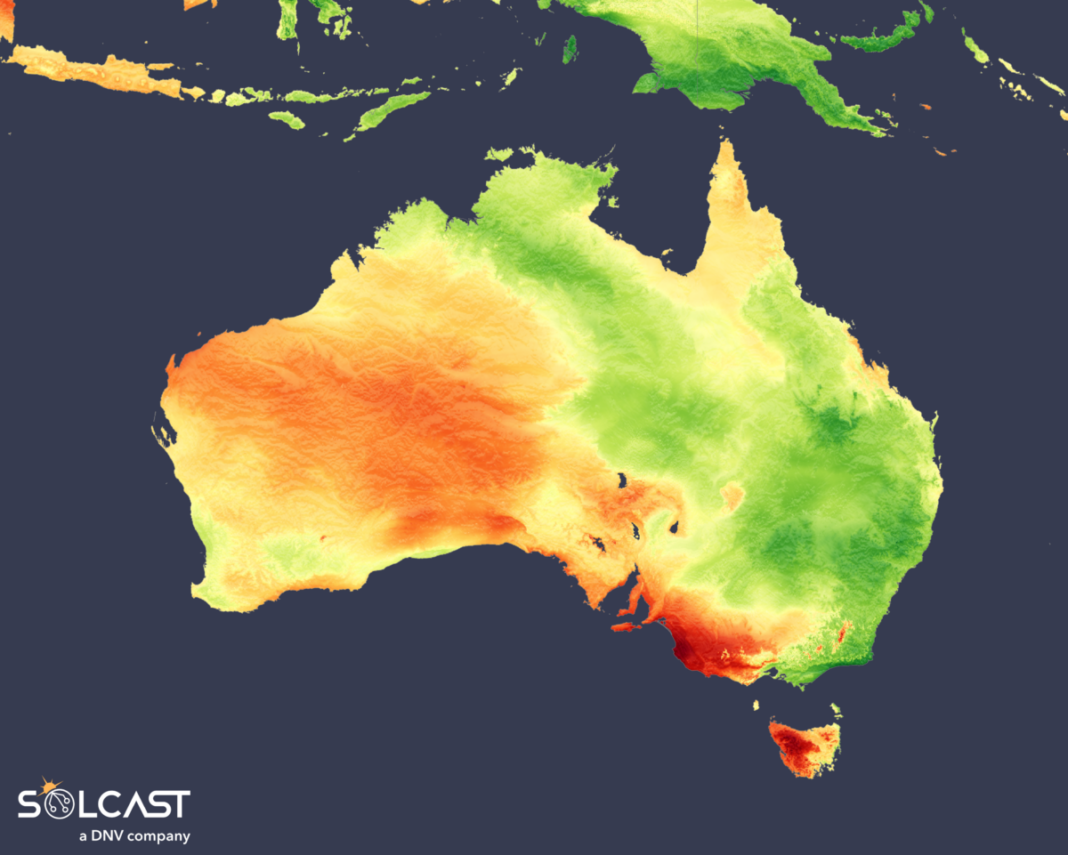
Unstable polar vortex situations and a persistent high-pressure system led to a interval of extreme climate throughout Australia in July and August, leading to each record-breaking chilly and warmth. These dynamic climate patterns carry combined results on photo voltaic irradiance, with massive variations between completely different areas, based on evaluation utilizing the Solcast API.

July was a difficult month for photo voltaic throughout a lot of Australia’s National Energy Market (NEM), as a lot of the inhabitants, targeting the east coast, skilled cloudier than traditional situations. This resulted in all however two states – Tasmania and South Australia – having decrease normalized behind-the-meter PV era than common in July. Western Australia recorded much less era as most of its put in capability was concentrated round Perth, which noticed beneath common irradiance. Meanwhile, virtually all areas of Queensland reported decrease than common irradiance, with reductions of as much as 10% in some areas.
In distinction, the western half of Australia enjoys increased than common irradiance, marking a transparent east-west division. The disparity is because of a near-record high-pressure system off the coast of Tasmania, which introduced record-breaking chilly to southeast Australia at first of the month. This chilly snap was quickly adopted by a collection of rain bands that additional decreased irradiance over a lot of the NEM.
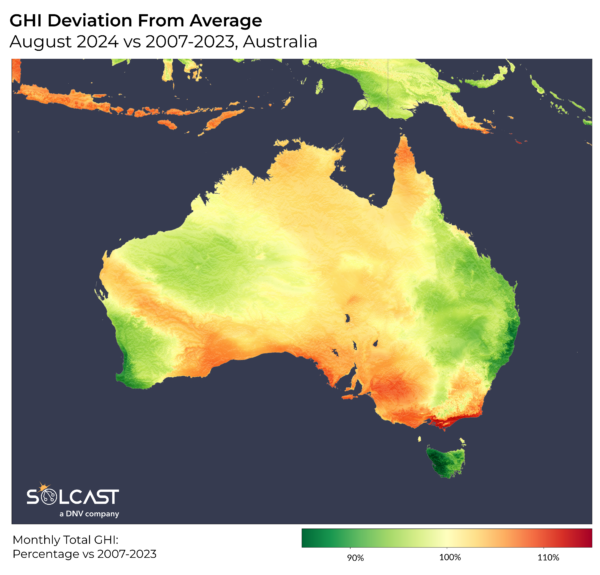
August confirmed a extra combined end result because of completely different climate patterns throughout the nation. Queensland, New South Wales, Tasmania and components of Western Australia skilled elevated cloud cowl and rain, dampening sunshine. However, the month ended with a rare rise in temperature, setting new winter data of over 40 diploma celsius in lots of locations. It is pushed by a high-pressure system over jap Australia and the Tasman Sea, which clears the sky and brings hotter air north. Despite this late rise in temperatures and clearer skies, earlier moist climate on the East Coast means general mild stays low.
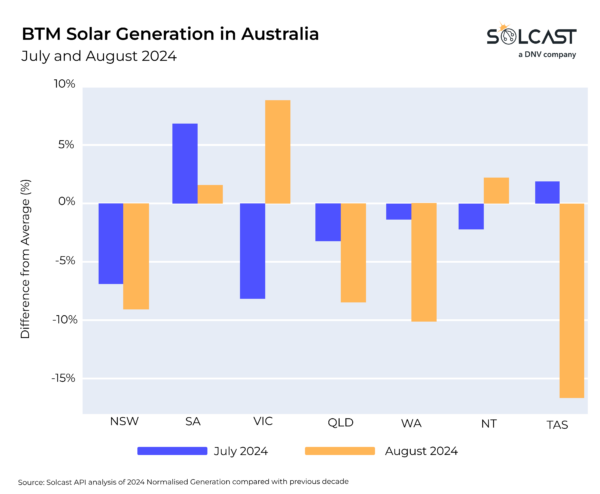
Victoria and the Northern Territory had a change of fortune, recording larger PV era than common in August, becoming a member of South Australia as the one states to see an enchancment. Meanwhile, Tasmania noticed the bottom normalized era within the final decade with the complete state experiencing decrease irradiance.
The sample of above common rainfall is anticipated to proceed by means of the remainder of the yr. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology is predicting the next probability of rain throughout a lot of central and jap Australia, which can proceed to have an effect on photo voltaic irradiance in these areas.
Solcast produces these numbers by monitoring clouds and aerosols at 1-2km decision around the globe, utilizing satellite tv for pc knowledge and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This knowledge is used to drive irradiance fashions, which allow Solcast to calculate irradiance at excessive decision, with a typical bias of lower than 2%, and likewise cloud monitoring forecasts. This knowledge is utilized by greater than 300 firms that handle greater than 150GW of photo voltaic belongings worldwide.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are these of the writer, and don’t essentially mirror these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
Popular content material

[ad_2]
Source link