[ad_1]
A analysis group from Japan and Indonesia used satellite tv for pc knowledge to research photo voltaic irradiance fluctuations within the Asia Pacific area and draw conclusions on which areas are best suited for future installations.
Researchers from Japan’s Chiba University and Indonesia’s Institut Teknologi Bandung used photo voltaic irradiance knowledge to achieve insights into the place to finest find future solar energy vegetation throughout the Asia Pacific.
The analysis paper, “Solar irradiance variability round Asia Pacific: Spatial and temporal perspective for lively use of photo voltaic power,” was printed within the July version of photo voltaic power, investigated the variation of photo voltaic irradiance by way of spatial and temporal heterogeneity.
The research used photo voltaic irradiance knowledge from the Japanese geostationary satellites Himawari-8 and Himawari-9 and Amaterasss, a instrument that estimates photo voltaic irradiance utilizing an ultra-high-speed calculation methodology with neural networks primarily based on a radiative switch mannequin. The knowledge obtained covers 2022 in 10-minute intervals, with a spatial decision of 0.04 levels, or roughly 4 km. The researchers additionally used a digital floor mannequin to grasp the distinction in photo voltaic irradiance at totally different altitudes.
Professor Hideaki Takenaka, who led the analysis, mentioned that evaluations primarily based on spatiotemporal knowledge “reveal traits which can be inconceivable to realize utilizing a standard methodology that depends on easy long-term averages or typical that meteorological 12 months as a typical photo voltaic irradiance knowledge.”
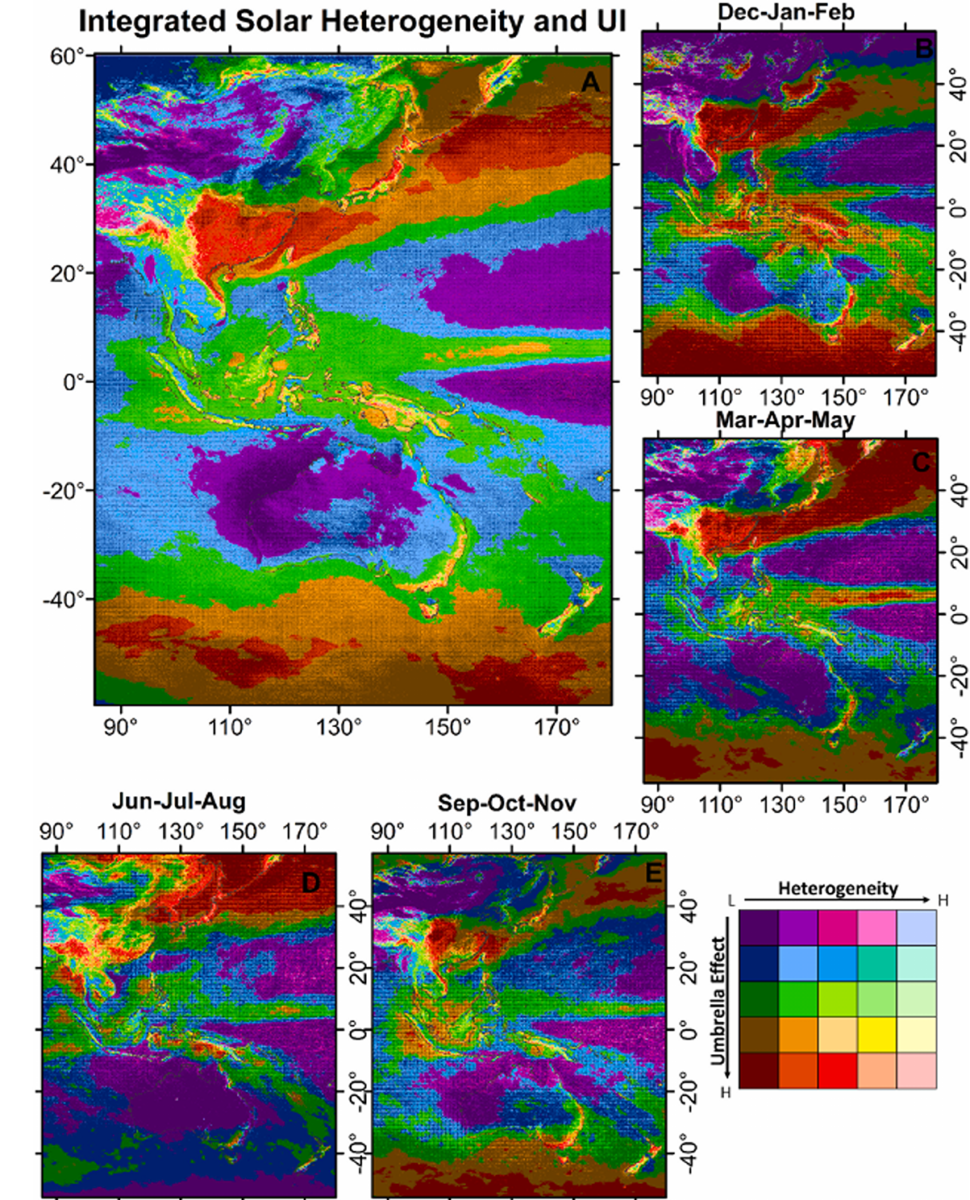
Each area is split into 0.2 levels × 0.2 levels or roughly 20 km × 20 km to find out its heterogeneity. The heterogeneity of photo voltaic irradiance in Asia Pacific is calculated to be about 0 to 135 W/m2.
The paper explains that photo voltaic heterogeneity exhibits seasonal variability, however places close to the equator expertise decrease fluctuations in photo voltaic irradiance over time in comparison with increased latitude areas, principally because of the results of rain and cloud exercise. Meanwhile, areas with increased elevations have increased heterogeneity on account of excessive cloud exercise, whereas oceans report the least heterogeneity.
The paper additionally calculated the likelihood of an umbrella impact brought on by clouds, often known as the umbrella impact index, at roughly 0 to 0.34 all year long. The researchers noticed the next umbrella index in excessive latitude areas throughout summer season than in winter. A big change in climate has been famous on the Tibetan Plateau, a broad, excessive plateau throughout the intersection of eight central, southern and japanese Asian international locations. This space has the bottom umbrella index in comparison with different durations from July to August.
Considering heterogeneity and the umbrella impact index enable researchers to advise the place future photo voltaic panels could also be appropriate. “An wonderful location for the set up of a solar energy plant has little heterogeneity and umbrella impact in time,” the analysis paper says. “Under these circumstances, the photo voltaic irradiance within the area has a excessive potential all year long because of the low cloudiness. In the goal space, 5.76% have these circumstances. Based on the outcomes, these circumstances may be present in desert and coastal areas at excessive altitudes.”
The scientists additionally discovered that 4.43% of the research space has low heterogeneity values however a excessive umbrella impact, and due to this fact probably the most unsuitable for photo voltaic installations.
The researchers additionally analyzed the efficiency of greater than 1,900 photo voltaic vegetation utilizing annual and seasonal knowledge. This evaluation discovered that many of the current solar energy vegetation are positioned in very low umbrella indices of the impression time in areas of low photo voltaic heterogeneity. Such places represent 39.17% of the full research space. However, a major a part of the present vegetation was discovered to not operate nicely from June to August, because of the umbrella impact brought on by the clouds. The researchers advise that these zones shouldn’t rely totally on solar energy to fulfill the elevated wants of those months.
In a dialogue of the optimum format for future solar energy vegetation, the analysis paper concludes that extra broadly distributed photo voltaic power era is superior to extra localized efforts and promotes rooftop photo voltaic as a key option to obtain elevated stability of photo voltaic power provide to the grid.
“Based on the spatial and temporal traits of photo voltaic irradiance, we suggest that it’s doable to stop fast fluctuations in solar energy era output by distributing small photovoltaic programs in a large place fairly than counting on massive solar energy vegetation,” mentioned Takenaka. “It’s price noting, these conclusions come from climate and local weather analysis, not an engineering perspective.”
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
Popular content material

[ad_2]
Source link