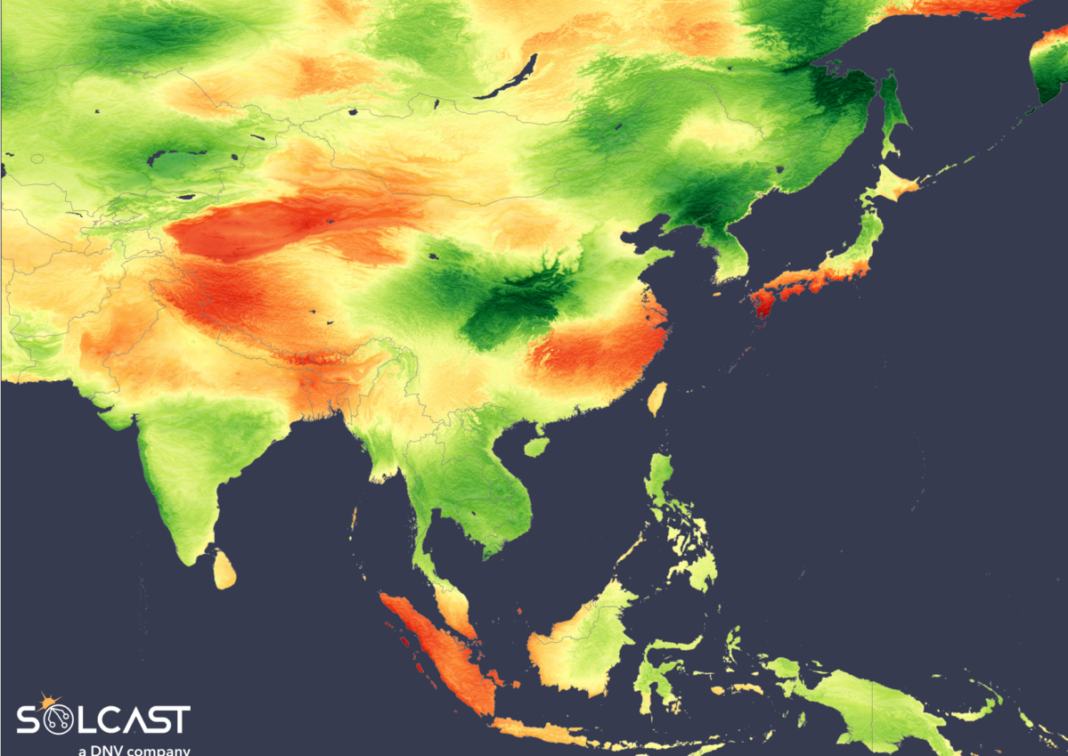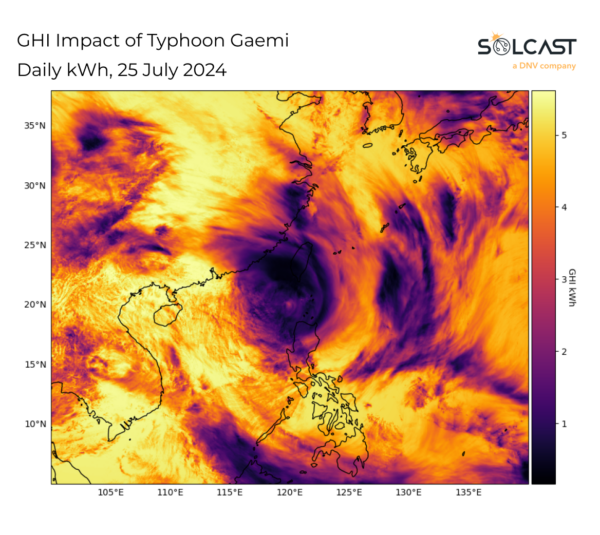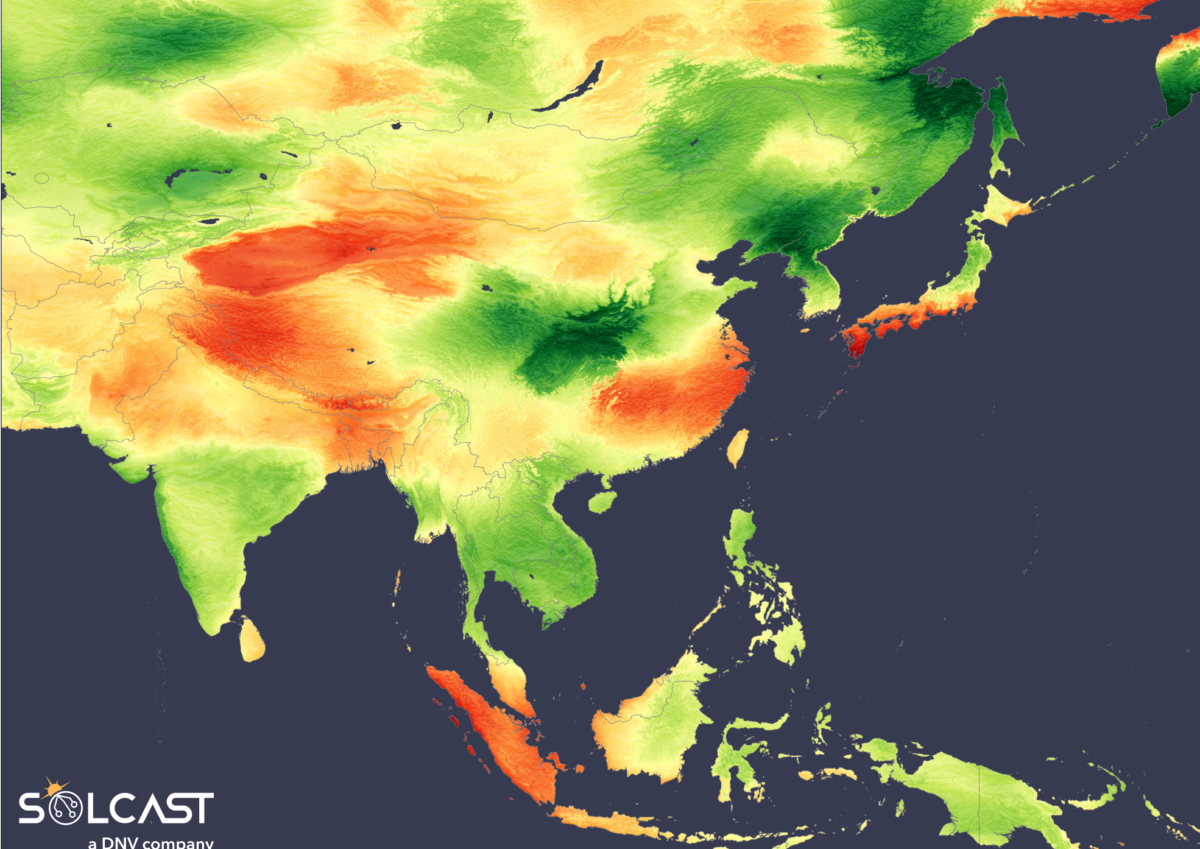
Different climate circumstances throughout Asia lead to totally different results on the July solar. Typhoon Gaemi led to lowered irradiance throughout the Philippines and a record-breaking monsoon season in India lowered common irradiance by 10% over a lot of the nation. Meanwhile, elements of China and Japan noticed elevated irradiance on account of a powerful subtropical ridge, in keeping with evaluation utilizing the Solcast API.
Along with sturdy winds that may destroy energy infrastructure, storms deliver heavy rain and clouds, resulting in lowered irradiance. Typhoon Gaemi was no exception, affecting irradiance ranges within the Philippines in mid-July. The month-to-month imply irradiance decreased by 10% from the long run July common.
Gaemi fashioned over the Pacific Ocean west of the Philippines, in an space with heat sea floor temperatures of 1 to 2 °C above July common.
Tracking northwest below the affect of the mid-atmospheric stress ridge, Typhoon Gaemi handed by means of the Philippines and proceeded to have an effect on Taiwan earlier than weakening in China’s Fujian province. The storm’s impact on irradiance alongside its path, Taiwan and most of China skilled a rise in sunshine within the first half of the month, with lower than half of the common rainfall resulting in common or above common irradiance for many of Eastern China.
India is experiencing an above-average monsoon season, with the monsoon spreading over the subcontinent on July 2, a couple of week sooner than standard. This early begin led to higher-than-normal rainfall in July, as moist southerly winds introduced heavy rain. Some areas noticed day by day rainfall averaging as much as 20mm, nearly double the same old quantity, leading to a ten% discount in irradiance within the south of the nation. The nation’s west coast was hit arduous, seeing the most important drop in irradiance, and Delhi broke a virtually 90-year document with 280mm of rain in a single day in June.
In distinction, China and Japan recorded their hottest July on document on account of an abnormally sturdy subtropical ridge. This atmospheric situation lowered the cloud cowl and led to a rise in daylight, leading to irradiance anomalies of greater than 15%. Temperatures soared above 38 levels celsius throughout Japan, whereas Hong Kong skilled a month-to-month minimal temperature of 28 levels celsius.
Solcast produces these numbers by monitoring clouds and aerosols at 1-2km decision around the globe, utilizing satellite tv for pc information and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This information is used to drive irradiance fashions, which allow Solcast to calculate irradiance at excessive decision, with a typical bias of lower than 2%, and in addition cloud monitoring forecasts. This information is utilized by greater than 300 corporations that handle greater than 150GW of photo voltaic belongings worldwide.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are these of the writer, and don’t essentially mirror these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].