[ad_1]
In a brand new weekly replace for pv journalSolcast, a DNV firm, reported that, all through July, smoke from wildfires in Canada and the US West Coast had a big impression on irradiance throughout North America, whereas Hurricane Beryl and atmospheric circumstances above delivered of unstable cloud cowl throughout the central and jap United States.
Throughout July, smoke from wildfires in Canada and the US West Coast considerably affected irradiance throughout North America, whereas Hurricane Beryl and higher atmospheric circumstances delivered unstable cloud cowl throughout the central and jap United States.
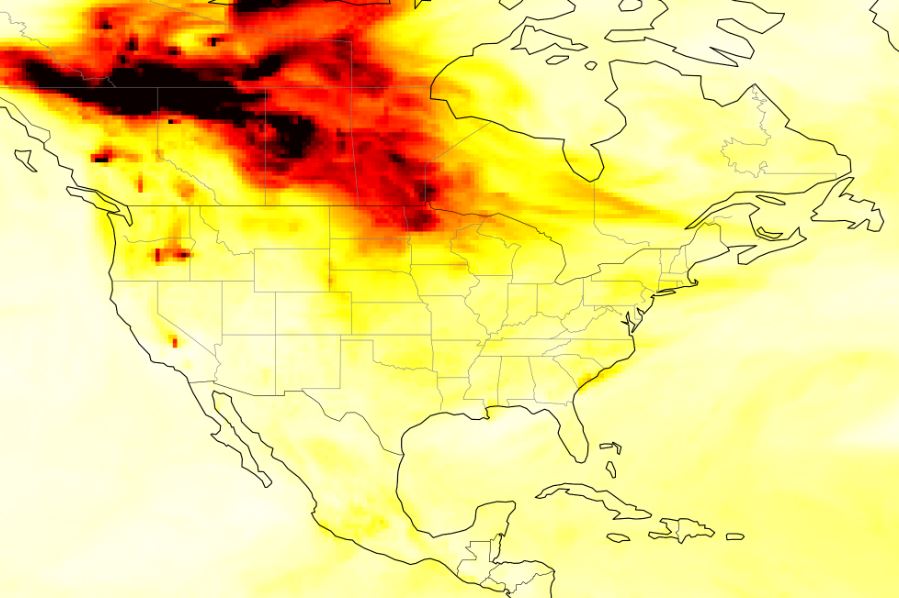
Analysis utilizing the Solcast API confirmed that the mixed results of diminished clearsky irradiance from smoke-related aerosols and cloud cowl led to irradiance ranges under 80% of long-term July averages on the Gulf Coast, East Coast , and within the Midwest. In distinction, robust atmospheric circumstances on the West Coast resulted in additional mild, extending by means of the Rockies to West Texas.
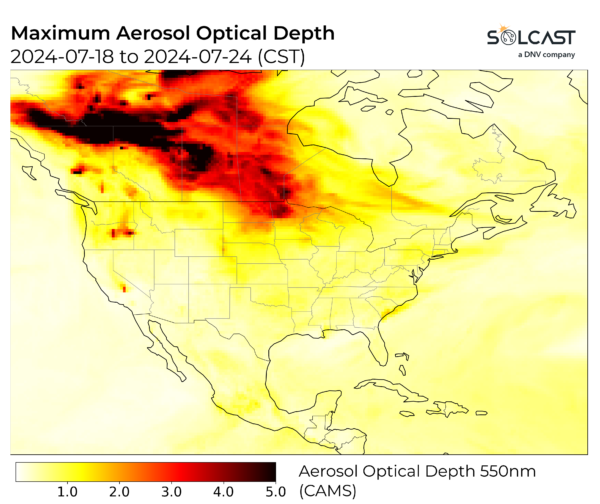
As the fires burned, atmospheric aerosols blew east and south, throughout the continent. Aerosols have an effect on irradiance by scattering and absorbing radiation within the ambiance, and cut back photo voltaic era even on a cloudless day. The peak ‘aerosol optical depth’, a measure of aerosol impact on irradiance, reveals the place the aerosol impact is strongest, and that smoke impacts the complete continent.
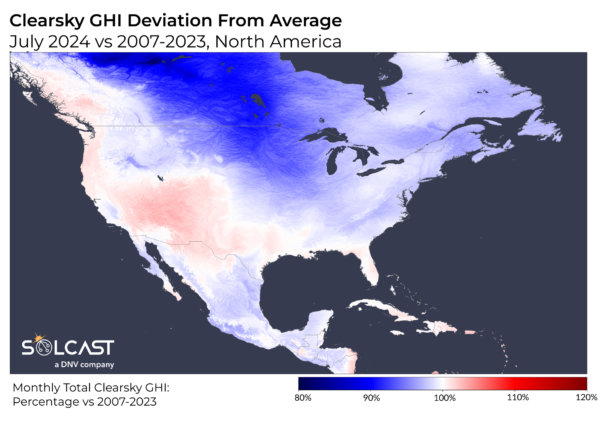
Low detection of clearsky irradiance (a measure of irradiance in entrance of a cloud or different climate occasion) down to twenty% in some areas of Canada close to the fires, indicating giant areas affected as smoke spreads within the ambiance. While in a standard month the impact of clouds and climate is increased than that of aerosols, the depth of this impact all through July is mirrored within the clear mild and the general GHI.
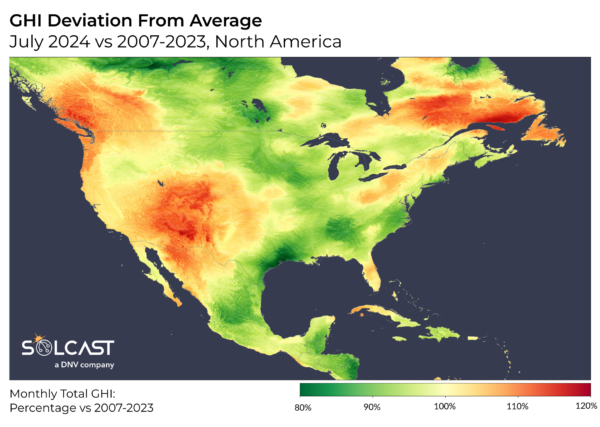
In addition to the fires, a robust upper-atmosphere dipole created clear and secure circumstances on the West Coast and unstable, cloudy circumstances on the East Coast. This results in irradiance ranges 10-20% above excessive averages in components of British Columbia, Washington State, California, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, New Mexico, and Western Texas. While these clear circumstances exacerbated the wildfires, the prevailing westerly winds saved the smoke from having a serious impression on these states. Conversely, the identical atmospheric circumstances led to instability on the East Coast, lowering irradiance within the Carolinas, Virginia, and components of New England. Hurricane Beryl additional affected irradiance, casting a big shadow over the Gulf Coast and South-East early within the month.
Solcast produces these numbers by monitoring clouds and aerosols at 1-2km decision world wide, utilizing satellite tv for pc information and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This information is used to drive irradiance fashions, which allow Solcast to calculate irradiance at excessive decision, with a typical bias of lower than 2%, and in addition cloud monitoring forecasts. This information is utilized by greater than 300 corporations that handle greater than 150GW of photo voltaic belongings worldwide.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are these of the creator, and don’t essentially replicate these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
Popular content material

[ad_2]
Source link