[ad_1]
Italian researchers designed a water-source warmth pump system meant for cooling, heating and home scorching water in social housing inventory constructed through the Nineteen Seventies–Nineties. The novel idea combines photovoltaic-thermal vitality with thermal storage and guarantees a seasonal coefficient of efficiency of 5.
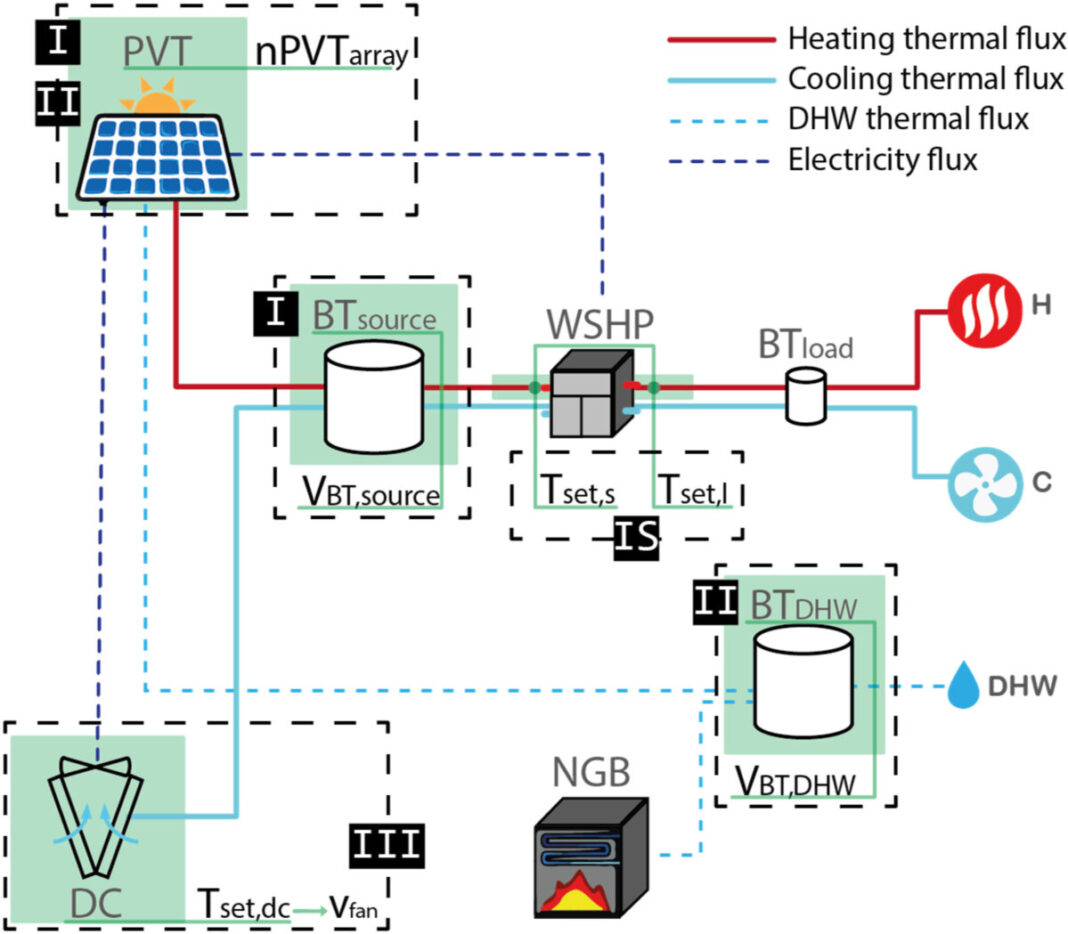
A bunch of researchers led by the Sapienza University of Rome has developed a brand new water-source warmth pump (WSHP) system that integrates photovoltaic-thermal (PVT) vitality and thermal vitality storage (TES) for the manufacturing of built-in heating, cooling, home scorching water manufacturing and electrical energy.
The system was created underneath the umbrella of the EU-funded RESHeat analysis venture, which goals to determine renewable and energy-efficient options for heating and cooling, in addition to home scorching water manufacturing in multi-apartment residential buildings. “This work is targeted on the Italian model of the RESHeat venture,” the scientists mentioned, noting that the proposed system adopts a scorching water storage tank as a substitute of underground warmth storage unit like variations of the system developed for European international locations at larger latitudes.
The system consists of a water-source warmth pump mixed with cooled photovoltaic panels, two storage models – one supply aspect and the opposite aspect load – and a fan coil. In the proposed system configuration, the low temperature warmth from the panels is used to fill the chilly properly of the warmth pump throughout heating. During cooling, the surplus warmth from the PV panels, which reaches the next temperature, is transmitted to the home scorching water manufacturing system.
“The PVT panels present thermal and electrical cogeneration, with {the electrical} vitality used to energy the WSHP, any backup heaters, auxiliary and condominium areas, whereas the low temperature warmth produced through the winter is used as a supply of WSHP by means of TES,” defined the analysis crew. “In distinction, besides through the heating season, from April to October, the warmth produced by the PVT is used for the manufacturing of DHW, which is saved within the devoted storage. Finally, through the summer time, the TES is related to a DC, essential to dissipate the surplus warmth produced by the HP for cooling the house.
Using TRNSYS software program and the multi standards resolution making (MCDM) methodology, the teachers carried out 184 simulations to find out the perfect dimension of system parts with the aim of deploying them in a social residential constructing with 13 residences in-built 1980 in Palombara Sabina, close to Rome, Italy.
“The reference pattern is the results of city planning began in Italy within the 60s of the ‘900 within the intervention program associated to social buildings earlier than the laws on the vitality efficiency of buildings,” they defined, including that the constructing, which at present depends on a centralized gasoline heating system, has a winter and summer time warmth load of 61 kW and 65 kW, respectively, and a DHW consumption of 55 l/individual for a complete which is 50 folks.
In MCDM simulations and evaluation, lecturers think about the principle parameters reminiscent of coefficient of efficiency (COP), photo voltaic fraction, fundamental vitality consumption, fundamental vitality financial savings, system and prices. in operation, in addition to the logistical-spatial standards. The researchers discovered that the most effective system configuration might be achieved utilizing 75 PVT panels with a complete of 25 kW divided into 15 strings, a buffer tank quantity related to the supply a part of HP which 3 m³, and a quantity of 1.5 m³ for DHW thermal storage. .
“The recognized temperature setpoints are 25 C for DC, whereas for HP, the 2 working temperatures of the evaporator and the condenser fluctuate in accordance with the exterior situations,” they additional defined. “On the chilly aspect, they vary from 7 to twenty C and fluctuate in accordance with the incident radiation and the warmth manufacturing at low temperatures of the PVT panels, whereas on the recent aspect, they fluctuate in accordance with the surface temperature.”
The system is described within the examine “Definition of a PVT coupled water supply warmth pump system by optimizing particular person parts,” printed in power.
“This work goals to make use of the constructing of Palombara Sabina as a pilot case for upgrading a central heating system for delicate climates, to suggest it as a perfect methodology that can be utilized in a big scale of the whole inventory of social housing constructed within the Nineteen Seventies- Nineties, with the aim of vitality conversion on an city scale,” the researchers concluded. “The targets are the effectivity of system, with a minimal seasonal COP of 5, and a minimal of 70% protection from renewable sources specializing in ambient temperature administration.”
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
Popular content material

[ad_2]
Source link