The Chinese in China used two sulfone-based natural molecules often known as diphenylsulfone (DPS) and 4,4′-dimethyldiphenylsulfone (DMPS) to passivate absorber defects in perovskite photo voltaic cells. The result’s a tool with the next electron cloud density on the interface between the perovskite materials and the passivation layer.
A bunch of researchers led by Zhejiang University of Technology in China proposed using two sulfone-based natural molecules often known as diphenylsulfone (DPS) and 4,4′-dimethyldiphenylsulfone (DMPS) to enhance the efficiency of perovskite. photo voltaic cells.
They used the molecules to enhance the cost distribution on the interface between the cell’s perovskite absorber and the passivation layer, which reportedly creates electron-rich techniques on the floor of the perovskite. Using density practical principle (DFT), a quantum-mechanical atomistic simulation technique to calculate a variety of properties of virtually any sort of atomic system, they simulated the cost density distributions of DPS interactions and DMPS with formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI).3) perovskite materials.
To research “Engineering an natural electron-rich floor passivation layer for environment friendly and secure perovskite photo voltaic cells,” printed in Cell Reports Physical Science, the scientists defined that the upper electron cloud density they present in DMPS creates a stronger bond between this materials and the perovskite absorber, which ends up in a greater cell stability. They additionally acknowledged that the electron-rich surroundings offered by DPS and DMPS reduces the constructive cost of lead (Pb) within the perovskite absorber, which contributes to the rise of the electron cloud density.
“These outcomes present that the uncoordinated Pb2+ The ions on the floor of the perovskite movie are successfully transmitted to the small molecules, which suggests an enchancment within the efficiency and stability of the cell,” the lecturers emphasised, noting that these outcomes have been confirmed by further evaluation accomplished by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic drive microscopy (AFM).
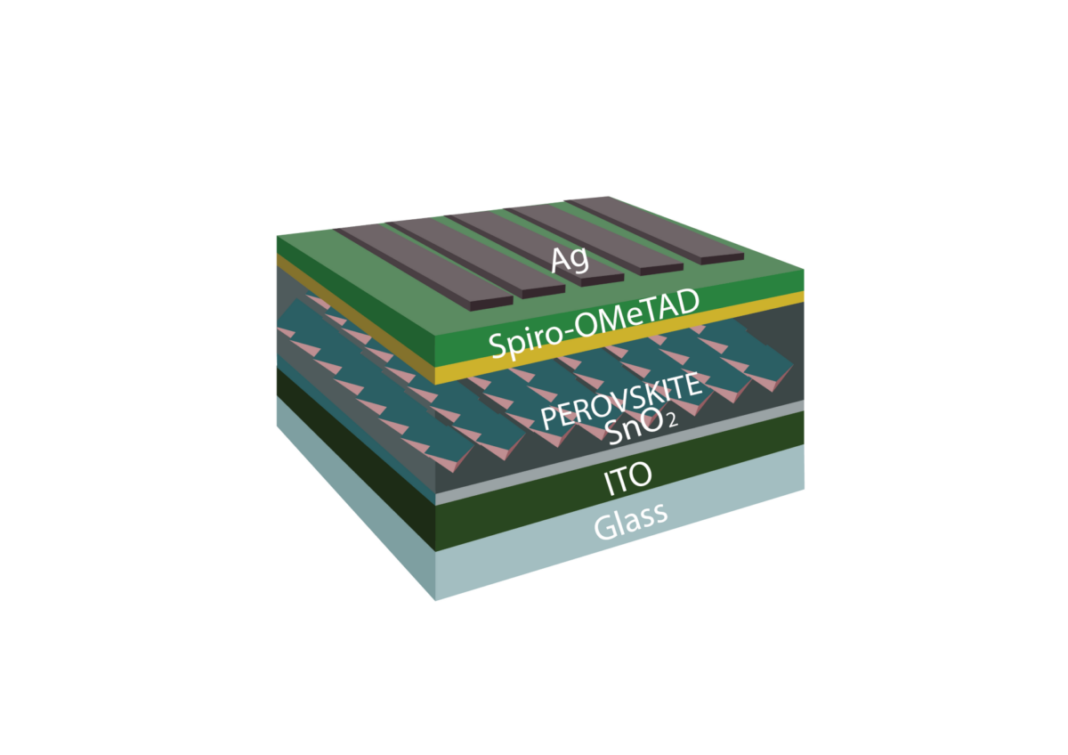
The proposed technique was additionally examined by constructing a bodily cell handled with DMPS and composed of a substrate made from glass and indium tin oxide (ITO), a tin oxide (SnO2) electron transport layer (ETL) , the cadmium-doped FAPbI3 absorber, a gap transport layer based mostly on Spiro-OMeTAD, and a silver (Ag) metallic contact. “An investigation of the impact of remedy focus on gadget efficiency revealed a big enchancment in photovoltaic efficiency at concentrations of 1 and three mg mL.-1 for DPS and DMPS, respectively,” the scientists mentioned.
The cell achieved an influence conversion effectivity of 23.27%, an open circuit voltage of 1.141 V, a short-circuit present density of 25.21 mA cm-2, and a fill issue of 80.93%. The gadget was additionally discovered to retain 92.5% of its preliminary effectivity after 1,000 hours. “The effectivity of the gadgets handled with DMPS elevated from the unique 21.21% to 23.27%,” the group highlighted, noting that the reference gadgets constructed with out DMPS and DPS remedy achieved a decrease outcomes.
“The floor modification technique utilizing environment friendly organically conjugated small molecules supplies a brand new technique to enhance the photovoltaic efficiency of perovskite photo voltaic cells, the researchers concluded.
Popular content material

This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].