[ad_1]
&bula; physics 17, 106
A theoretical mannequin for the illumination of photosynthesizing algae in large clams suggests rules for extremely environment friendly daylight assortment.
Crops on a farm solely seize about 3% of obtainable photo voltaic vitality, a lot lower than the 20%–25% captured by massive photo voltaic arrays. Now a analysis workforce has used a theoretical mannequin to clarify efficiencies as excessive as 67% for photosynthesizing algae hosted by large clams. [1]. Researchers argue that clams obtain this efficiency with an optimized geometry. Mollusks also can alter the spacing of algae clusters in accordance with altering gentle circumstances. The researchers hope that understanding clams’ photo voltaic effectivity could assist different scientists enhance the effectivity of photo voltaic know-how and clarify facets of photosynthetic conduct in different ecosystems similar to forests.
A photosynthetic cell can convert virtually all incoming photons into usable vitality, says biophysicist Alison Sweeney of Yale University. But the effectivity is decrease in massive methods like agricultural farms. “Can we obtain near-perfect effectivity in lots of areas of the earth? This is an pressing query” as researchers attempt to cut back dependence on fossil fuels, Sweeney stated.
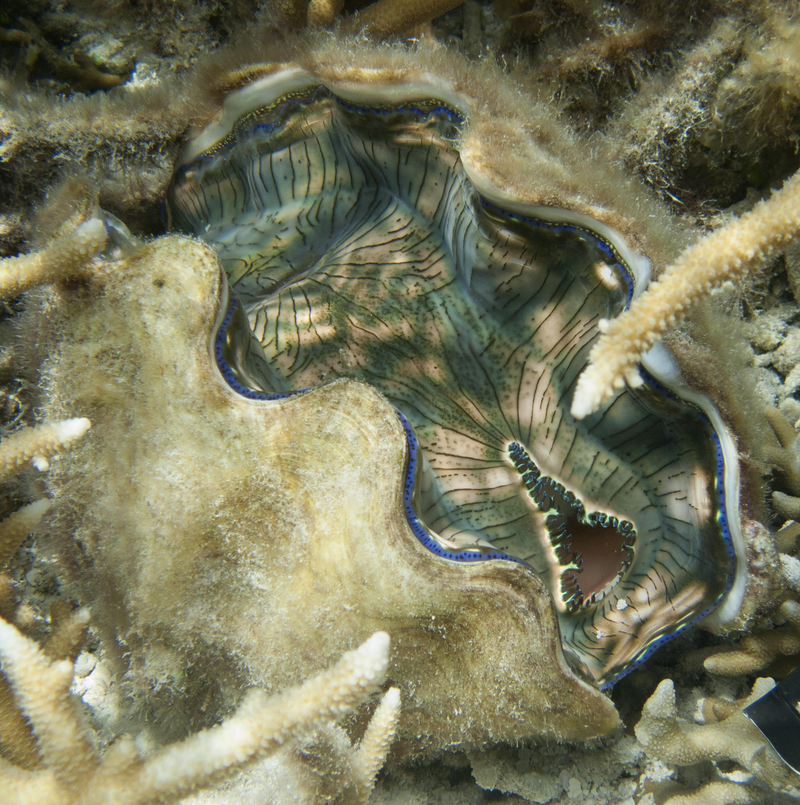
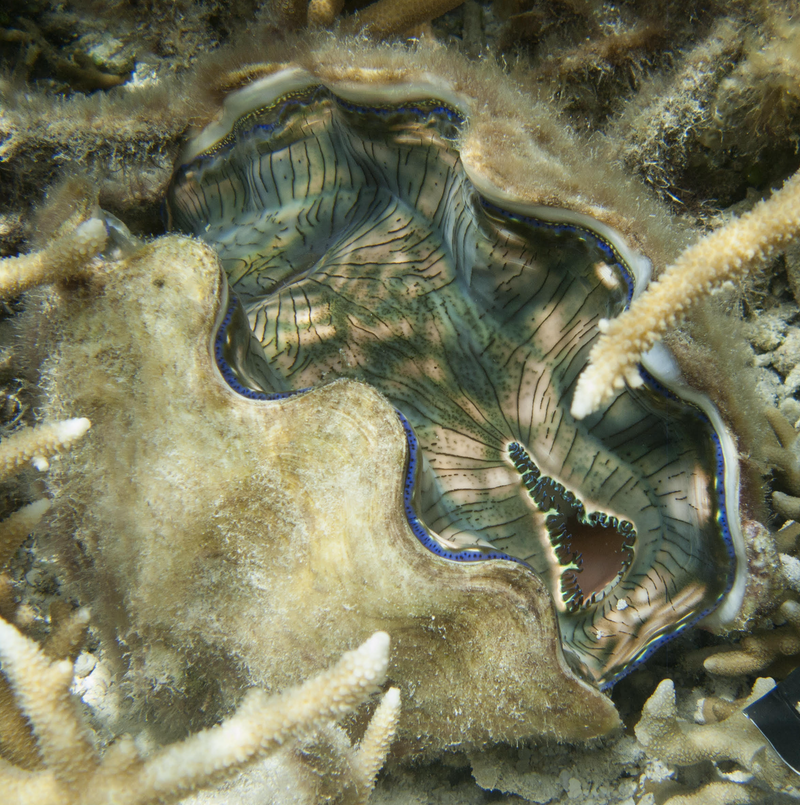
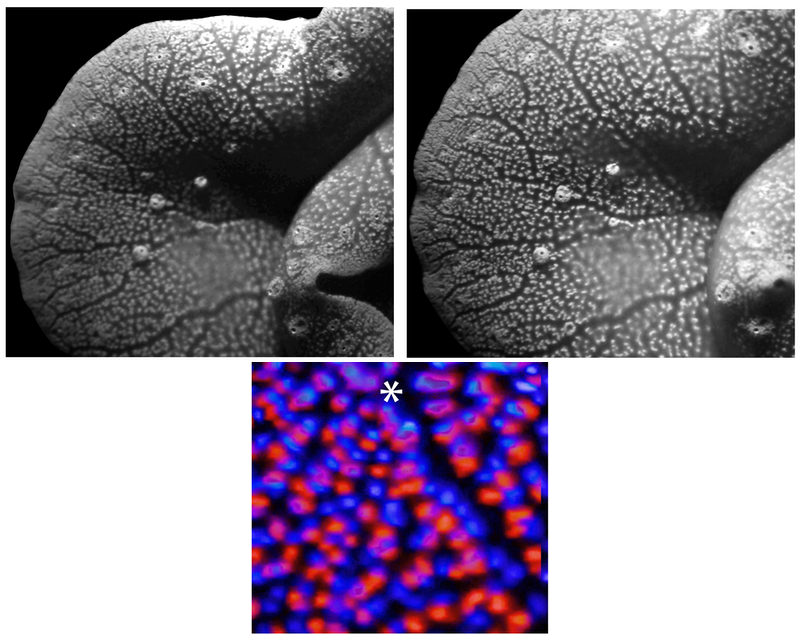
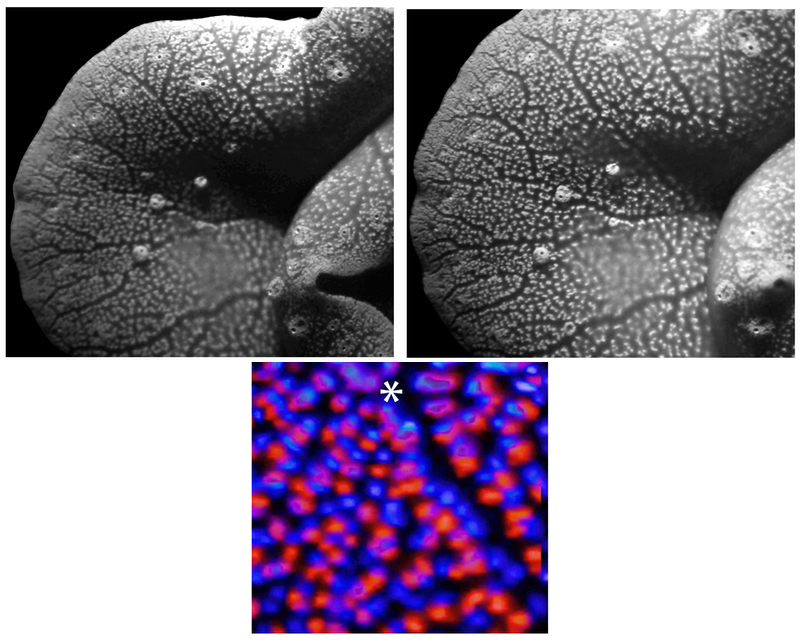
Looking for environment friendly designs, Sweeney and colleagues regarded to massive clams, which develop as much as 4 ft throughout, due to symbiotic algae that produce a few of the clam’s important vitamins. The algae reside in 100-µm-wide vertical columns inside the interior tissues of the clam that attain the perimeters of the shell and obtain daylight by way of the opening of the shell. This gentle diffuses by way of a layer of translucent cells on the floor after which descends the algal column the place the sunshine is absorbed for photosynthesis.
In earlier work, Sweeney and his colleagues discovered that the translucent layer of cells diffuses gentle in a manner that spreads it out horizontally—what the researchers name melting—and that provides even gentle to the vertical surfaces of the algal column. This gentle permits environment friendly photosynthesis deep within the tissue [2].
Now they’ve developed a mathematical mannequin for the method of absorbing photo voltaic vitality. This mannequin accounts for the change within the spatial distribution and depth of sunshine because it travels by way of the clam tissue and captures how the general effectivity of photosynthesis relies on a number of elements. Algal cells harvest low depth gentle extra effectively than excessive depth gentle. In addition, the spatial variation of depth all through the tissue relies on the distribution of algal cells, every of which absorbs photons. To mannequin photosynthesis biochemistry, Sweeney and colleagues used a well-tested set of equations.
In the simulations, the researchers estimated the overall photosynthetic productiveness of their mannequin system for various gentle intensities and geometries. Their simulations additionally explored two completely different potential preparations of algal cells: randomly distributed all through the amount and concentrated in slim columns separated by clear tissue, like actual ones. clams. Researchers have discovered that columnar group is usually extra environment friendly at harvesting gentle, in some instances not less than 10 occasions extra environment friendly.
The benefit of the columnar group, says Sweeney, is that every algal cell experiences virtually the identical gentle, due to the translucent layer. In distinction, the random association causes a lot of the gentle to be absorbed by the shallowest layers, leaving little for the algae at higher depths.
The mixture of the translucent layer and the columnar association led to an effectivity of 43%, however to succeed in the 67% effectivity measured in experimental research, the workforce had so as to add a further factor to the simulations. The optimum distance between the columns relies on the depth of the incoming gentle, which varies all through the day. Because clams can inflate and deflate their tissues by way of modifications in blood strain in response to the touch, researchers speculate that they might additionally use this skill to regulate the spacing of the algal column. in response to modifications in lighting. The inclusion of such an adaptive technique of their mannequin results in an vitality effectivity that matches the observations.
This perception into the environment friendly photosynthetic geometry of the large clam could assist enhance solar-energy manufacturing, particularly for biofuels, by way of large-scale algal plantations, in accordance with Sweeney and his colleagues. They additionally consider that some forests could already be exploiting a technique just like the large clam. The cloud cowl layer generally discovered above spruce forests can play the identical position because the layer of translucent cells.
“We suppose it is potential that within the forest, particular person spruce bushes can play the structural and optical position of particular person columns of algae within the clam system,” Sweeney stated. If so, forests could obtain increased photosynthetic efficiencies than crop fields, though it will require extra research to find out.
“This examine expands the thoughts,” says biophysicist Philip Nelson of the University of Pennsylvania. “And the authors make a shocking leap throughout disciplines to counsel that gentle distribution in a big quantity helps not solely meter-sized clams but additionally kilometer-sized ones. boreal forest.”
—Mark Buchanan
Mark Buchanan is a contract science author who divides his time between Abergavenny, UK, and Notre Dame de Courson, France.
References
- AL Holt and so forth.“Simple mechanism for environment friendly gentle utilization in photosynthesis impressed by large clams,” PRX Energy 3023014 (2024).
- AL Holt and so forth.“Photosymbiotic large clams are photo voltaic flux transformers,” JR Soc. Interface. 1120140678 (2014).
Subject Areas
[ad_2]
Source link