[ad_1]
Reliable evaluation of native photo voltaic radiation sources is a key a part of large-scale PV energy plant undertaking growth and financing. This evaluation is often primarily based on the belief that the long-term common annual photo voltaic radiation from earlier years is just not considerably totally different from the anticipated future photo voltaic useful resource availability. In many areas of the world, the provision of photo voltaic radiation in 2023 will probably be a lot greater (as much as 10-12%) than the long-term common, and this may increasingly overshadow the truth that a big fraction of utilities- scale PV energy plant underperforming.
Björn Müller and colleagues printed a paper within the ISES Solar Energy Journal that discusses points surrounding useful resource analysis of photo voltaic irradiation within the context of long-term variations generally known as “international dimming and brightening.”
They hypothesize that as a result of long-term traits that will exceed the time of previous observations and the deliberate lifetime of a solar energy plant, a paradigm shift will be proposed: as a substitute of (or maybe on high of) utilizing probably the most lengthy attainable time. to calculate a mean worth, solely the ten most up-to-date years needs to be used as an estimate for future photo voltaic irradiation.
In their 2014 article, utilizing knowledge from the German Meteorological Service from eight commentary stations throughout Germany with greater than 40 years of Global Horizontal Irradiation (GHI), the time for the dimming interval was decided to be longer. from the start of the info set 1951, to 1983, whereas the shining interval began in 1984 till the top of the info set in 2010.
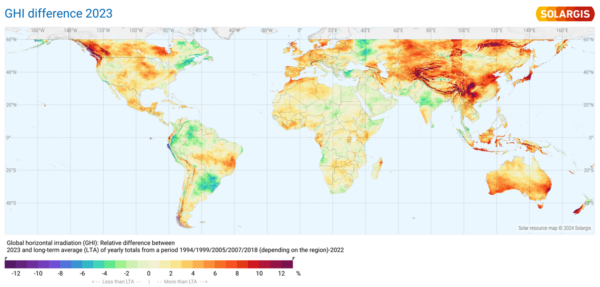
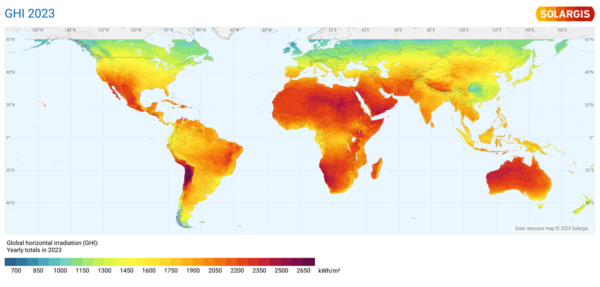
Solargis® just lately printed a GHI set of photo voltaic maps exhibiting that photo voltaic irradiation in 2023 will probably be greater than the long-term common (LTA) of the annual complete from a interval from 1994 to 2022 (with totally different begin dates relying on the area). The maps under present (high) the % deviation of the annual GHI in 2023 in comparison with the long-term common (GHI distinction 2023) and (backside) the GHI for 2023.
Detailed regional maps, spanning totally different intervals relying on the area, are additionally obtainable on the Solargis® web site. GHI is crucial climate issue affecting the power manufacturing of photo voltaic photovoltaic energy vegetation. Having dependable and up-to-date details about GHI is vital to know whether or not the solar energy plant is performing as anticipated or not.
Solar irradiation maps exhibiting latest GHI values such because the 2023 map can be utilized as a preliminary and approximate reference, and it’ll assist determine the necessity to run a extra detailed power verify if the map values don’t fall inside the beforehand anticipated values. , or if the map values don’t match the on-site observations and the precise power era, for PV vegetation already in operation.
In these instances, a brand new estimate of the anticipated long-term photo voltaic useful resource, together with an up to date month-to-month change evaluation, could also be needed, and a assessment of on-site photo voltaic irradiance sensors and a cautious examination of attainable sources of poor efficiency of. the PV plant could also be required.
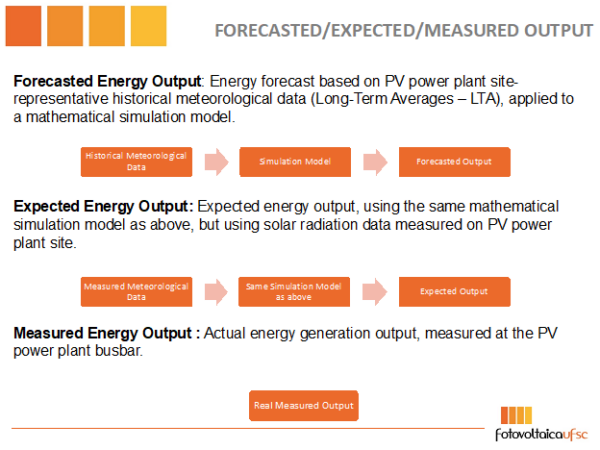
What is the distinction between predicted, anticipated and measured power manufacturing?
The Energy Performance Index (EPI) of a solar energy plant is a metric used to evaluate the general output power efficiency and effectivity of the plant. It often represents the ratio of the particular power output of the solar energy plant to the theoretical or anticipated power output underneath ultimate situations, making an allowance for elements corresponding to the provision of photo voltaic radiation, system losses, and elements in surgical procedure.
The EPI calculation can range relying on the particular context and methodology used, however often includes evaluating the precise power manufacturing of the solar energy plant over a time frame (corresponding to a month or a yr) to the anticipated power manufacturing primarily based on elements corresponding to PV put in capability, website photo voltaic radiation ranges, system effectivity, and different efficiency parameters. The determine under illustrates the distinction between the anticipated, anticipated, and measured power manufacturing of a solar energy plant.
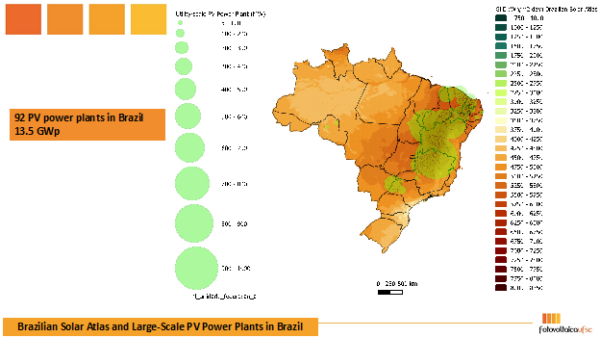
Many massive PV energy vegetation around the globe are underperforming attributable to numerous technical causes. The EPI of many vegetation within the massive portfolio (near 4 GWp) analyzed by the Fotovoltaica/UFSC laboratory in Brazil is under the anticipated efficiency, at a stage similar to the optimistic variations seen within the Solargis® maps.
The picture under from the Brazilian Solar Atlas, the place all massive PV energy vegetation (5 to 1000 MW) are superimposed on the photo voltaic irradiation map, reveals that almost all of them are within the area the place the photo voltaic irradiation in 2023 will probably be 4 to eight % of upper than the long-term common of the annual complete from 1999 to 2022, canceling out and masking the poor efficiency of those belongings.
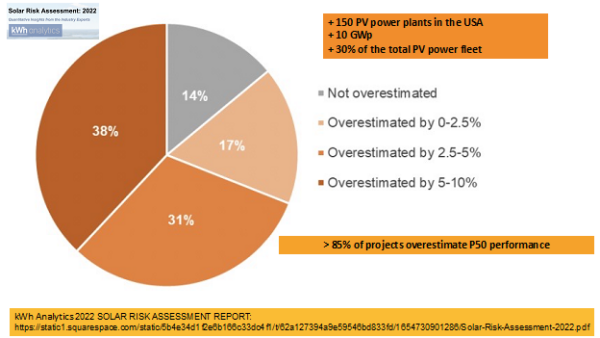
A latest Solar Risk Assessment report printed by kWh Analytics reveals that one in three photo voltaic belongings within the USA exceeds the P50 estimate by greater than 5%, as proven within the picture under. In Australia, the place for a number of days every year photo voltaic and wind farms are sometimes shut down for just a few hours attributable to destructive costs, many massive PV vegetation are additionally underperforming, however it’s troublesome to take away this data.
The EPI metric is utilized in PV energy plant monitoring, efficiency evaluation and analysis of contractual power output; PV undertaking output certification and PV energy plant due diligence; PV energy plant commissioning and subject efficiency analysis. If photo voltaic PV is to retain its fame as a low-risk asset class with predictable and secure long-term money flows, massive PV energy vegetation should function at excessive EPI ranges that have to be thought-about to extend in photo voltaic radiation availability. as proven in 2023.
Authors: Prof. Ricardo Rüther (UFSC), Prof. Andrew Blakers / ANU
ISES, the International Solar Energy Society is a UN-accredited membership NGO based in 1954 working in the direction of a world with 100% renewable power for all, used effectively and properly.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are these of the writer, and don’t essentially mirror these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link



