[ad_1]
In the brand new weekly replace for pv journal, Solcast, a DNV firm, reviews that the climate in April in Europe exhibits a north-south division affecting photo voltaic era throughout the continent. High strain techniques within the Mediterranean imply sunnier than regular situations in Southern Europe, which advantages PV output.
The April climate in Europe exhibits a north-south divide affecting photo voltaic era throughout the continent. High strain techniques within the Mediterranean imply sunnier than regular situations in Southern Europe, which advantages PV output. A succession of low strain techniques within the north resulted in cloudier climate affecting photo voltaic era. Around the Mediterranean, there are some mud transport occasions in April, the place the mud within the air impacts the irradiance, and the air pollution can have an effect on the era, however these 1-2 day occasions should not seen within the month-to-month common .
Sunnier situations are loved within the Iberian Peninsula and across the Mediterranean and the Black Sea, with irradiance ranges reaching 15-20% above the long run April averages. Solar property in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Turkey, Greece, Spain, Portugal, and components of Italy profit from these situations. The enhance in irradiance ranges is because of clear skies and good climate introduced by larger than common strain for this time of 12 months.
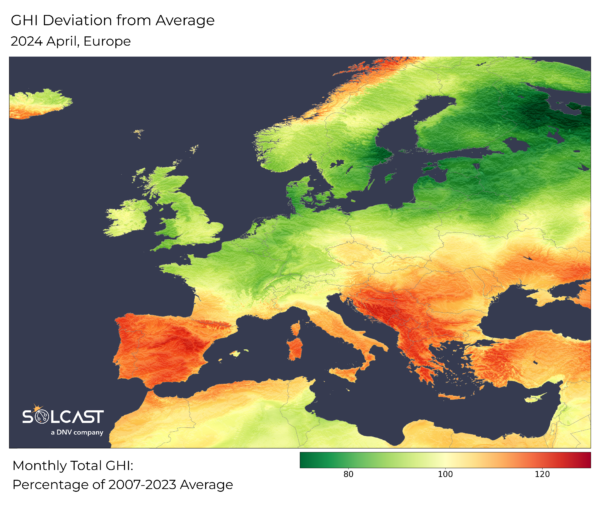
In distinction, April was a cloudy and wet month for northern Europe leading to a lower in PV era. This cloud is pushed by a sequence of low strain techniques throughout the area from the North Sea, which explains the 15-20% under common irradiance within the Baltic States, Finland, Sweden, Denmark, Germany, France (no in relation to the south), the Benelux Countries, the United Kingdom, and Switzerland. The Baltic States and Finland had been hit the toughest, with irradiance 20% under regular, which equates to a mean of simply 3kWh/day of irradiance.
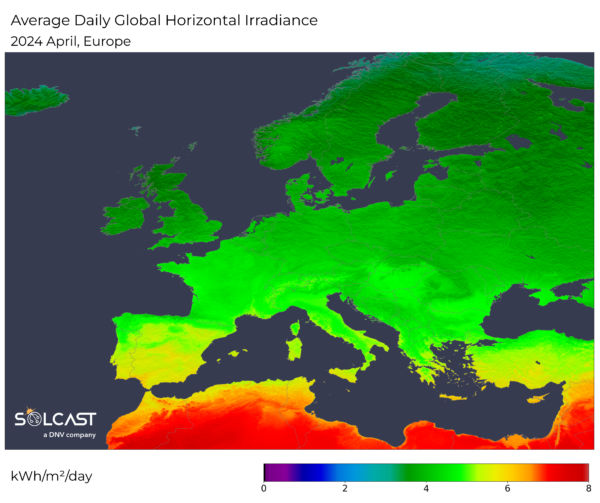
In distinction to the final degree of irradiance in northern Europe, the northern a part of Norway acquired 10% greater than regular irradiance. This could also be attributable to low strain techniques shifting within the south, lowering the same old cloudiness within the far northern areas. However, the seemingly influence of photo voltaic manufacturing right here is small, as a result of the irradiance in these northern latitudes is simply 3.0-3.5kWh / day, and the areas are sparsely populated.
There had been a number of situations of Saharan mud transport to Europe in April. It occurred in early April all through Spain, and 23/24 April in Greece and Ukraine, inflicting the native irradiance to lower by as much as 25% of the each day irradiance. Due to the quick period of those occasions, they aren’t mirrored within the month-to-month common irradiance, however the mud polluted from these occasions might have a longer-term impact on PV era.
Solcast produces these numbers by monitoring clouds and aerosols at 1-2km decision all over the world, utilizing satellite tv for pc information and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This information is used to drive irradiance fashions, which allow Solcast to calculate irradiance at excessive decision, with a typical bias of lower than 2%, and likewise cloud monitoring forecasts. This information is utilized by greater than 300 corporations that handle greater than 150GW of photo voltaic property worldwide.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are these of the creator, and don’t essentially replicate these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link