[ad_1]
In the brand new weekly replace for pv journalSolcast, a DNV firm, experiences that heat sea floor temperatures and disturbances enhance coastal moisture alongside China’s southern coast, which in flip will increase photo voltaic irradiance by 5-15% at excessive altitudes. time period common.
Asia’s March climate patterns noticed dramatic modifications resulting from jet stream actions and an prolonged monsoon season, affecting photo voltaic power potential throughout the area, in keeping with evaluation utilizing Solcast API.
In Japan, the southward shift of the jet stream led to a rise in photo voltaic irradiance in Hokkaido, the place ranges have been 10-20% larger than standard in March. This uncommon sunshine within the northern island is completely different from the situations within the southern islands equivalent to Okinawa, the place
irradiance dropped as much as 10% beneath common resulting from enhanced low-pressure methods channeling Pacific moisture and elevated cloud cowl.
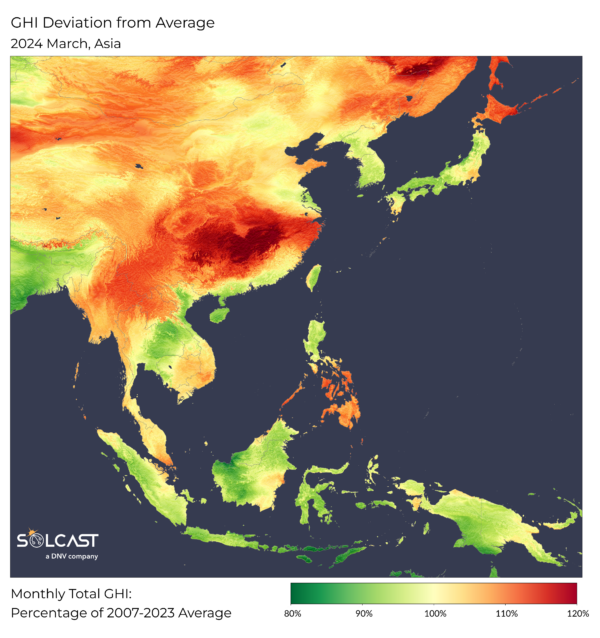
South Korea, protected by Japan from the brunt of those moist Pacific methods, skilled solely a slight lower in photo voltaic irradiance. This small change highlights the native nature of climate results on photo voltaic power sources, highlighting the significance of high-resolution climate information for power modeling.
The South China Sea additionally performs an vital position in shaping climate patterns this season. Warm sea floor temperatures and disturbances enhance coastal moisture alongside the southern coast of China, and go away little cloud cowl in southern Vietnam and the southern Philippines, growing irradiance by 5-15% at excessive altitudes. time period averages. Inland China, regardless of ongoing giant forest fires in Sichuan, has recorded a major 10-20% enhance in irradiance, resulting from decreased aerosol masses in comparison with earlier many years.
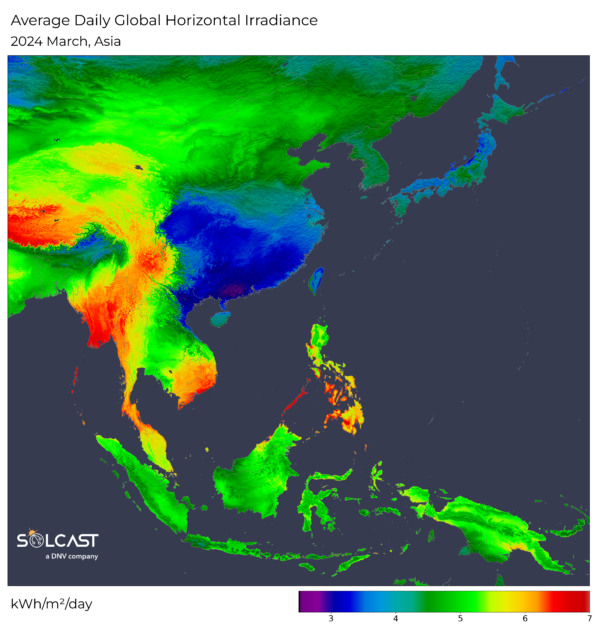
Meanwhile, the Southern Hemisphere skilled an extended than regular wet season, affecting photo voltaic irradiance in Malaysia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea, the place ranges have been 5-15% beneath common. This very long time brings not solely decline
irradiance but in addition will increase rainfall, which complicates the manufacturing of photo voltaic power.
These findings spotlight the vital affect of atmospheric phenomena on photo voltaic power era. The potential to foretell and analyze these modifications is crucial for managing photo voltaic power sources successfully, particularly in a climate-diverse area like Asia. As climate patterns proceed to evolve, the combination of correct meteorological information and forecasting will grow to be more and more vital in optimizing photo voltaic power methods throughout the continent.
Solcast produces these numbers by monitoring clouds and aerosols at 1-2km decision all over the world, utilizing satellite tv for pc information and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This information is used to drive irradiance fashions, which allow Solcast to calculate irradiance at excessive decision, with a typical bias of lower than 2%, and likewise cloud monitoring forecasts. This information is utilized by greater than 300 corporations that handle greater than 150GW of photo voltaic belongings worldwide.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are these of the writer, and don’t essentially mirror these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link