[ad_1]
Scientists in Spain have developed a semi-online approach to foretell photo voltaic irradiance at completely different places inside a photovoltaic plant. The proposed coaching methodology is outlined as appropriate for extremely variable time sequence forecasting.
Researchers from the University of Seville in Spain have developed a brand new machine studying algorithm for predicting very quick photo voltaic irradiance. Its enter is predicated on the preprocessing of sensor knowledge, utilizing temporal and spatial correlation evaluation of cloud motion.
“Short-term or short-term electrical energy manufacturing forecasting can assist in areas corresponding to real-time system monitoring, electrical energy pricing, or avoiding system overload,” they mentioned. “More encouragement is within the regulatory area. More and extra nations require wind and photovoltaic turbines to offer what are referred to as ancillary companies, that are important actions for the protected and dependable operation of the methods. of electrical energy.
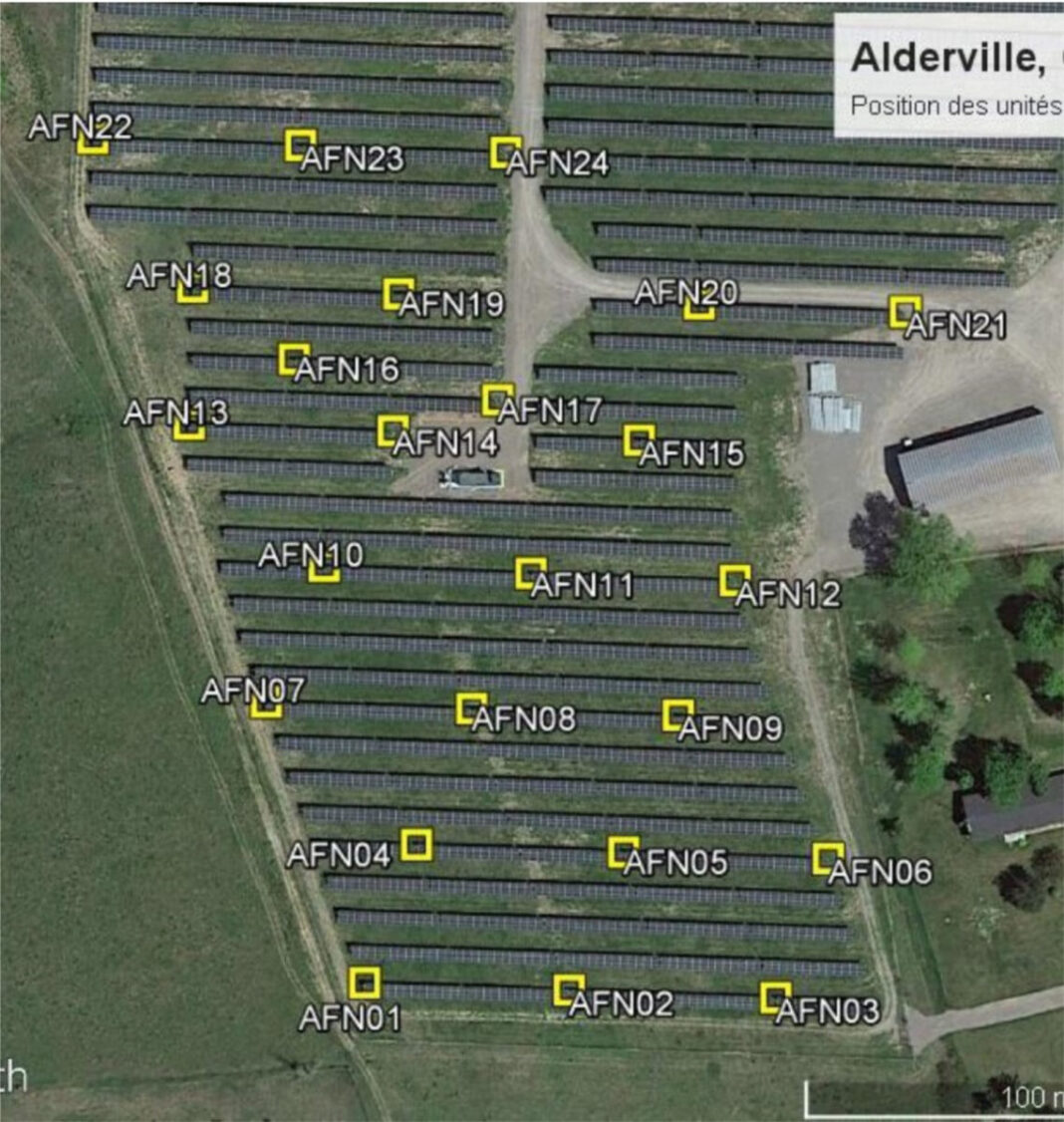
The dataset used for mannequin growth comes from a web based repository of the Alderville 5 MW photo voltaic farm in southeastern Canada. In explicit, it consists of 24 photo voltaic PV panels that present irradiance knowledge each 1 ms on days with variable and really variable cloudiness.
While the analysis group centered on the prediction horizons of 15 s and 30 s, it created a correlation evaluation to know the relationships between the panels at completely different occasions. To do this, they checked the correlation of every panel’s measured irradiance with all the opposite panels. Then they evaluated the correlation with completely different time lags.
“The panels within the neighborhood present larger correlations as a result of they’re influenced by the identical cloud patterns, whereas the panels positioned on the extremes of the wind path axis present decrease correlations due to their positioning inside the gradient of the cloud evolution,” the group defined.
Accounting for time lag and panel correlation, the researchers then fed the info into three machine studying methods: eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGB), Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LGBM), and Random Forest (RF).” The system is known as semi-online as a result of the inference is finished in actual time, however the mannequin coaching shouldn’t be executed incrementally each time. Instead, it’s educated in very small units of situations,” the researchers emphasised.
“Slightly superior outcomes have been achieved in LGBM in comparison with XGB and RF, though the variations weren’t important,” they added. “On the variable day itself, a imply absolute share error (MAPE) of 4.411 was obtained within the worst situation (30 s forecast horizon of the cluster positioned upstream) and a couple of.483 in probably the most favorable situation (15 s forecast horizon) within the cluster. positioned beneath).”
Looking forward, teachers plan to find out precisely how far into the long run the system can present correct outcomes and analyze the system’s response to sudden modifications in wind path.
Their findings are offered in “Semi-real-time choice tree ensemble algorithms for very short-term photo voltaic irradiance forecastin”, revealed in International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
Popular content material

[ad_2]
Source link