[ad_1]
The novel photo voltaic cell makes use of tungsten sulfide because the again floor subject layer. According to its creators, this layer could be included into typical CIGS photo voltaic cells to enhance their effectivity and cut back the price of the absorber materials.
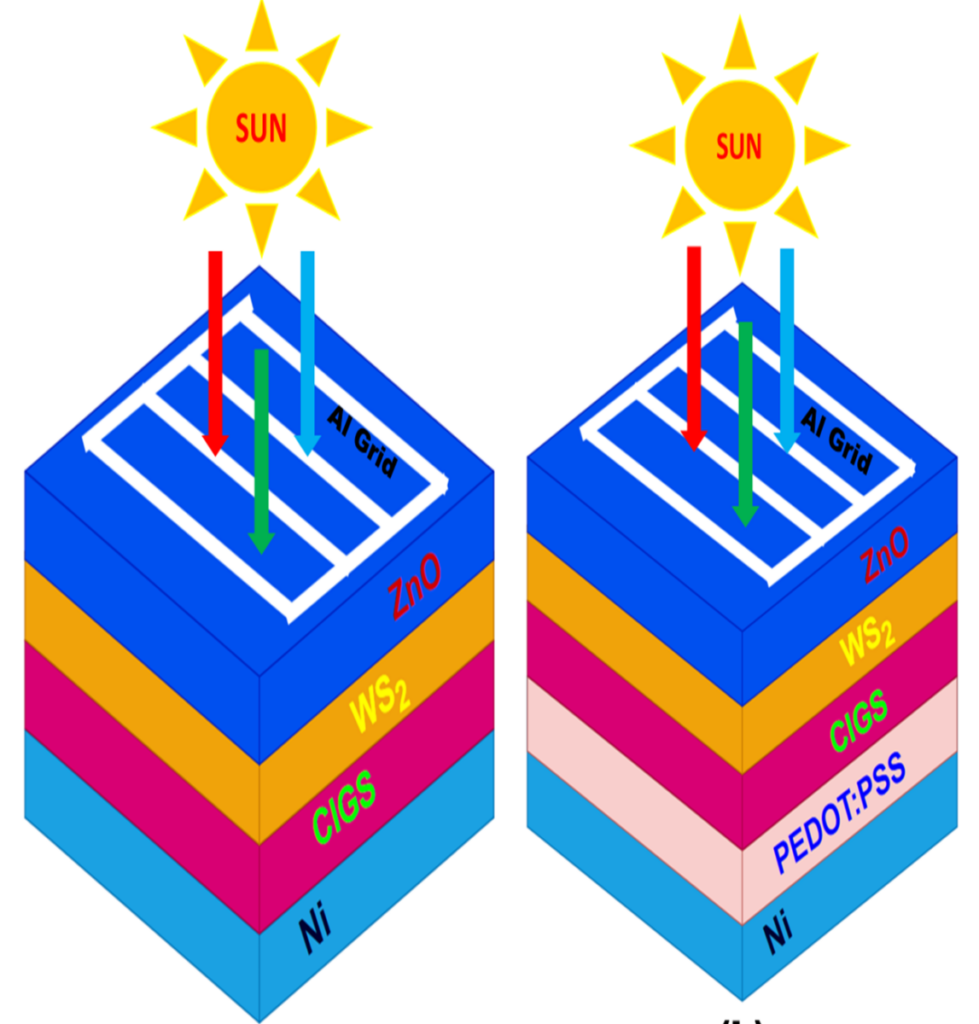
Researchers from India’s Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology have proposed a brand new copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) photo voltaic cell construction utilizing tungsten disulfide (WS).2) because the again floor subject (BSF) layer.
BSF layers encompass a greater doped area on the again facet of the photo voltaic cell and is often used to extend the voltage of the system. WS2 – a particularly slick, dry movie lubricant coating that operates in harsh circumstances – can be utilized in photo voltaic cells as an electron transport layer or buffer layer, and nanosheets and nanoparticles ready from digital WS2 Powders are generally utilized in nanoelectronics, optoelectronics, gas-sensing gadgets, hydrogen evolution reactions and vitality storage gadgets.
“The novelty of this analysis work is that for the primary time by means of simulation work, within the historical past of CIGS photo voltaic cells, a 25.70% effectivity was obtained with a 200 nm CIGS absorber layer thickness and 50 nm again floor subject layer thickness,” the corresponding writer of the analysis, Sushma M. His faceSPOKE pv journal.
He additionally defined that lowering the thickness of CIGS cells is aimed toward lowering the consumption of uncommon earth supplies equivalent to indium and gallium, in addition to their value per watt. “This impact could be seen on the mass manufacturing scale of CIGS photo voltaic cells,” he added. “This sort of construction has not been reported earlier to the most effective of the authors’ data.”
Used by scientists the SCAPS-1D photo voltaic cell capability software program, developed on the University of Ghent, to simulate the novel cell configuration. They imagine that the cell depends on a again contact layer fabricated from nickel (Ni), a PEDOT:PSS layer, a CIGS absorber, a buffer layer fabricated from WS2a window layer primarily based on zinc oxide (ZnO), and a entrance electrode fabricated from aluminum (Al).
“The BSF layer, positioned behind the cell, reduces the recombination of cost carriers, equivalent to electrons and holes, which in flip reduces the lack of carriers,” mentioned the group. “Another key contribution is meditation; right here, a part of the incident mild could be mirrored into the cell by means of the BSF layer in its capability as a reflective layer. Improving the trail of sunshine contained in the cell improves absorption and will increase present manufacturing.”
The scientists simulated the efficiency of the system below commonplace illumination circumstances and located that it achieved an influence conversion effectivity of 25.7%, open-circuit voltage of 0.81 V, short-circuit present density of 39.33 mA /cm2, and fill issue of 79.89%.
“At a defect density of 10 cm3 for the CIGS absorber layer, the system offers the most effective output, and from the collection and shunt resistance variation, it’s confirmed {that a} low worth of the collection resistance and better shunt resistance is favorable for higher efficiency,” they additional defined.
The novel cell idea is offered within the paper “Design and simulation of a brand new extremely environment friendly ultra-thin CIGS photo voltaic cell system construction: A plan to cut back the associated fee per watt worth,” just lately printed in Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content material
[ad_2]
Source link