[ad_1]
The researchers have outlined a “scalable” manufacturing course of that reportedly leads to a tungsten diselenide movie with an effectivity of as much as 22.3%. The proposed method facilitates mass manufacturing of high-efficiency multilayer WSe2 photo voltaic cells at low value.
A crew of researchers led by Stanford University has developed a brand new manufacturing course of to construct transition metallic dichalcogenide (TMD) photo voltaic cells in a scalable method, thus bringing them nearer to business manufacturing.
TMDs are two-dimensional supplies with distinctive semiconducting properties and excessive optical absorption coeffiscientists. This makes them appropriate for the manufacturing of semi-transparent and versatile photo voltaic cells with potential functions in aerospace, structure, electrical autos, and wearable electronics, the place mild weight, a excessive power-per -weight ratio, and adaptability are extremely fascinating.
“We have developed a scalable, mass production-friendly methodology that may yield photovoltaic-grade, wafer-scale tungsten diselenide (WSe).2) movies with a layered van der Waals construction and superior traits, together with cost service lifetimes of as much as 144 ns, greater than 14 instances longer than every other large-area TMD movies beforehand demonstrated. ,” the corresponding writer of the research, Koosha Nassiri Nazif, spoke pv journal.
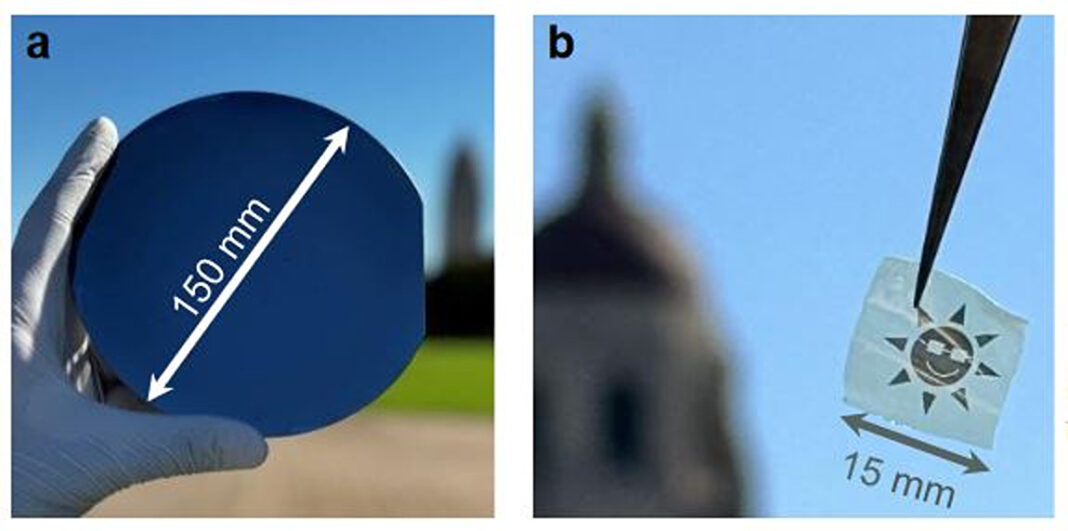
The group designed a sputtered multilayer WSe2 movie with a thickness of 15−30 nm for functions on a 150 mm wafer by way of a selenization course of based mostly on a solid-source selenium (SS-Se) in 900 C or low-thermal-budget hydrogen selenied (H2Se) precursors at 650 C. The ensuing WSe2 movie has an power bandgap of 1.2 eV to 1.3 eV, which scientists describe as near splendid for photo voltaic power harvesting.
The movie reportedly displays superior traits in comparison with earlier selenization reviews, in addition to clean and uniform surfaces. According to the researchers, with improved contacts and doping, it’s doable to attain an effectivity of as much as 22.3% in an optimized photo voltaic cell design.
“Our lifelike fashions present that such service lifetimes correspond to about 22% energy conversion effectivity and about 64 W g-1 particular energy of a packaged photo voltaic cell, or roughly 3 W g-1 in a totally packaged photo voltaic module. The outcomes of this research will facilitate the mass manufacturing of high-efficiency multilayer WSe2 photo voltaic cell at low value,” Nassiri Nazif expressed.
The novel cell idea is described within the paper “Towards Mass Production of Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Solar Cells: Scalable Growth of Photovoltaic-Grade Multilayer WSe2 by Tungsten Selenization,” which was not too long ago revealed in ACS Nano. The analysis crew contains teachers from the University of Colorado Boulder and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) of the US Department of Energy, in addition to from Hasselt University and the University of Antwerp in Belgium,
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
Popular content material

[ad_2]
Source link