[ad_1]
Chinese researchers declare to have developed an “ultrastable” perovskite photo voltaic cell primarily based on a two-dimensional, Dion-Jacobson section perovskite. The gadget is made utilizing blade coating expertise and is scalable, in response to its creators.
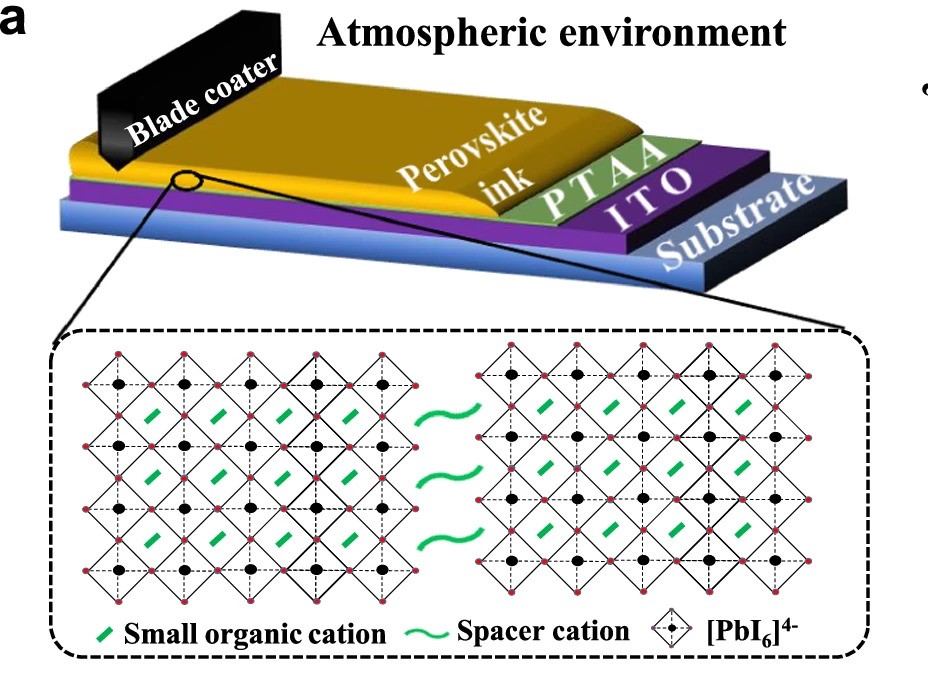
Researchers led by China’s National Center for Nanoscience and Technology have developed a 2D Dion-Jacobson (DJ) perovskite photo voltaic cell that reportedly displays a excessive stage of stability whereas attaining an influence conversion effectivity of 19.11 %.
Two-dimensional (2D) Dion-Jacobson (DJ) perovskite phases have aroused the curiosity of the scientific group attributable to their stability towards harsh environmental circumstances and their aggressive efficiency in optoelectronic purposes. Solar cells primarily based on DJ perovskites, nevertheless, present comparatively poor efficiency in comparison with their 3D counterparts.
For its cell, the Chinese group used a perovskite materials often called (CDMA)(MA)n−1PbnI3n+1, the place CDMA stands for 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanammonium. “Structural analyzes present that these supplies have a singular small interlayer-displacement quantum-well configuration that differs from most DJ perovskites, which may scale back the interlayer areas and tune the their mutual alignment to facilitate interlayer cost transport and structural stability,” the researchers defined.
The gadget is constructed utilizing blade coating expertise and is scalable, in response to teachers. It is constructed utilizing a substrate manufactured from glass and indium tin oxide (ITO), a gap transport layer (HTL) primarily based on poly[bis(4-phenyl)(256-trimethylphenyl)amine(PTAA)CDMA-basedDJperovskitelayerusakabuckminsterfullerene(C60)electrontransportlayer(ETL)abathocuproine(BCP)bufferlayerandatopelectrodethatismadeofsilver(Ag)[bis(4-phenyl)(256-trimethylphenyl)amine(PTAA)CDMA-basedDJperovskitelayerabuckminsterfullerene(C60)electrontransportlayer(ETL)abathocuproine(BCP)bufferlayerandtopelectrodemadeofsilver(Ag)[bis(4-phenyl)(256-trimethylphenyl)amine(PTAA)CDMA-basesaDJperovskitelayerusakabuckminsterfullerene(C60)electrontransportlayer(ETL)usakabathocuproine(BCP)bufferlayerugusakatopelectrodengahinimosapilak(Ag)[bis(4-phenyl)(256-trimethylphenyl)amine(PTAA)CDMA-basedDJperovskitelayerabuckminsterfullerene(C60)electrontransportlayer(ETL)abathocuproine(BCP)bufferlayerandatopelectrodemadeofsilver(Ag)
For reference, the group also produced a similar cell with a modified DJ perovskite layer. While the novel structure is based on CDMA, the reference cell is based on PDMA, which means 1,4-phenylenedimethanammonium. PDMA DJ has a similar organic molecular configuration to CDMA materials, but it is more widely studied.
Tested under standard lighting conditions, the CDMA DJ cell achieved an efficiency of 19.11%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.16 V, a short-circuit current density of 20.41 mA cm−2 , and a fill factor of 80.56%. The reference PDMA DJ device obtained an efficiency of 14.87%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.06 V, a short-circuit current density of 18.32 mA cm−2, and a fill factor of 76.46%.
“Importantly, the fabricated cells also exhibit exceptional humidity, thermal, and operational stability,” the group emphasized. “After storing it in a 90% relative humidity (RH) or 85 C continuous aging condition for more than 4000 hours and 5000 hours, respectively, the devices show an 8% degradation for the humidity stability test and negligible efficiency loss for thermal stability measurement.In particular, the operational stability under continuous light stress shows a small loss of efficiency of more than 6000 h.
At the end of the article, the scientists added that “the designed interlayer-displacement DJ series provides an important and potential pathway for the construction of new structurally stable 2D perovskites. The use of blade-coating in the designed that DJ perovskite solar cells may prompt new developments in scalable technology and their commercialization process.
The new cell architecture is introduced in “Ultrastable and efficient slight-interlayerdisplacement 2D Dion-Jacobson perovskite solar cells,” published in Communication in Nature. The research team includes scientists from China’s National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, the University of South China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Beijing Technology And Business University, and the Beihang University.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and want to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content
[ad_2]
Source link