[ad_1]
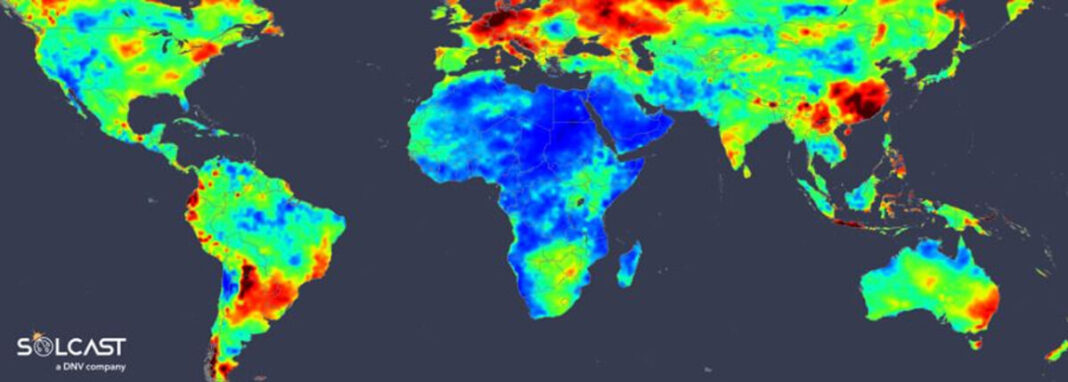
In the brand new weekly replace for pv journalSolcast, a DNV firm, reviews that the areas with the very best year-to-year variability in irradiance embody Central and Northern Europe, East Coast Australia, Northern Argentina, and China, with Africa exhibits the strongest irradiance year-on-year. .
Understanding year-to-year variability in photo voltaic power potential is important for grid planning and storage optimization. An evaluation utilizing the Solcast API reveals the areas with essentially the most vital variations in irradiance from 12 months to 12 months. This information is made by wanting on the decadal variability, evaluating the vary of complete annual irradiance to the common irradiance of every location. Interestingly, areas with excessive intra-day cloud variability don’t essentially have the best inter-annual variability.
Regions with the very best year-to-year variability in irradiance embody Central and Northern Europe, East Coast Australia, Northern Argentina, and China. Africa exhibits the strongest irradiance year-on-year.

In Central and Northern Europe, the excessive variability of irradiance is as a result of dominance of continental winds within the South and East or maritime air plenty from the Atlantic, Arctic, and Mediterranean. The Iberian Peninsula, nevertheless, experiences little variability as a result of comparatively fixed mixing of Atlantic and Mediterranean air plenty.
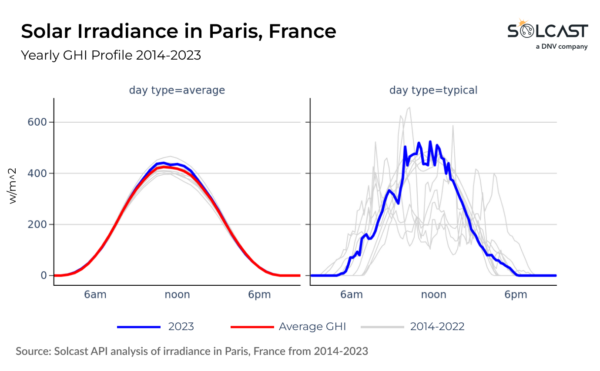
North America presents average variability within the Gulf Coast, Midwest, and Northeast areas, influenced by the interplay of Gulf of Mexico moisture, monitoring of the jap Pacific frontal system, and Atlantic air mass. In comparability, the Rockies and West Coast stand out
comparatively steady year-to-year irradiance, dominated by westerly airflow from the Pacific.

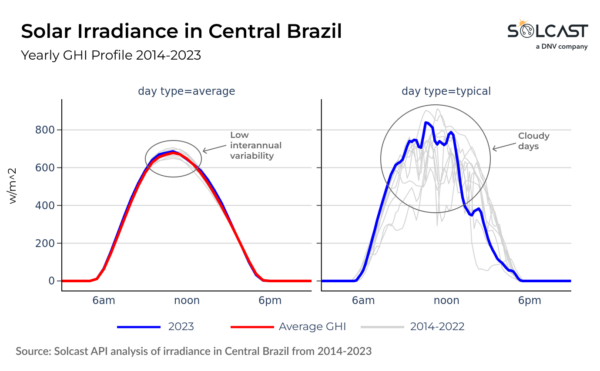
South America presents a distinct situation. Despite excessive diurnal variability attributable to cloudiness and precipitation, the Amazon area maintains a remarkably fixed quantity of cloud cowl from 12 months to 12 months, leading to steady complete annual irradiance. The Atacama Plateau, just like
Saharan Africa, is unusually steady as a result of low cloud cowl. In Northern Argentina, massive modifications in interannual irradiance are noticed, relying on how the Pacific frontal techniques work together with the Andes mountains.
In India, the overall irradiance within the western area varies from 12 months to 12 months attributable to much less common and constant rainfall in comparison with the east. China’s massive irradiance variability is partly pushed by modifications in aerosol masses over the previous decade, with jap Asia experiencing modest year-to-year modifications.
Saharan Africa and the Middle East present the least variability in interannual irradiance, dominated by cloudless desert circumstances. Sub-Saharan Africa, regardless of the tropical monsoon, stays fixed from 12 months to 12 months. However, Southern Africa experiences elevated variability as a result of interplay between tropical and mid-latitude climate techniques.
The Sunda Islands in Indonesia present excessive variations in irradiance as a result of transitions of the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) and the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), which vastly have an effect on the depth and length of the biennial monsoon. .

East Coast Australia experiences excessive variability as a result of teleconnections of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which additionally influences the variability of the northwest coast of South America. The deserts of Central Australia usually are not very sunny in comparison with different deserts, such because the Sahara, the Middle East, and the Atacama Plateau as a result of impact of ENSO. In distinction, northern tropical Australia has comparatively steady irradiance between years as a result of moderating affect of a constant dry season that outweighs the variability of the moist season.
Solcast produces these numbers by monitoring clouds and aerosols at 1-2km decision world wide, utilizing satellite tv for pc information and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This information is used to drive irradiance fashions, which allow Solcast to calculate irradiance at excessive decision, with a typical bias of lower than 2%, and likewise cloud monitoring forecasts. This information is utilized by greater than 300 corporations that handle greater than 150GW of photo voltaic property worldwide.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are these of the creator, and don’t essentially mirror these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
Popular content material

[ad_2]
Source link