[ad_1]
An worldwide analysis group has analyzed an important obstacles that stop antimony trisulfide photo voltaic cells from attaining passable energy conversion effectivity and proposed a collection of optimization parameters which can carry it nearer to business manufacturing.
An worldwide analysis group led by the Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission has developed a brand new design for thin-film photo voltaic cells based mostly on antimony trisulfide (Sb).2S3)
This sort of cell typology, in the meanwhile, is way from reaching business manufacturing because of the low crystallinity and excessive resistivity of Sb2S3 movie, which impacts effectivity. However Sb2S3 has a great bandgap, from 1.70 to 1.90 eV, and a outstanding mild absorption coefficient, and stays a promising materials for future PV cell purposes.
With this in thoughts, researchers have investigated the transport mechanisms, resistance, and defects of Sb2S3 cells. “The novelty of this work lies within the detailed theoretical evaluation of Sb2S3 photo voltaic cells, notably specializing in the intricate interaction of various transport mechanisms similar to tunneling-enhanced recombination, Sb2S3/CdS interface recombination, and non-radiative recombination,” they defined.
To tackle these obstacles, the analysis group adopted a modeling framework to research transport mechanisms and their interactions. “The important aim of this research is an in depth dedication of the dominant mechanism of recombination,” it says, noting that different components affecting a Sb2S3 cell effectivity is the doping of the cadmium sulfide (CdS) layer, thickness, bandgap, and affinity.
The scientists additionally investigated the consequences of shunt resistance (Rs) and collection resistance (Rs) on cell efficiency, in addition to the impact of CdS/Sb interfacial defects2S3 interface.
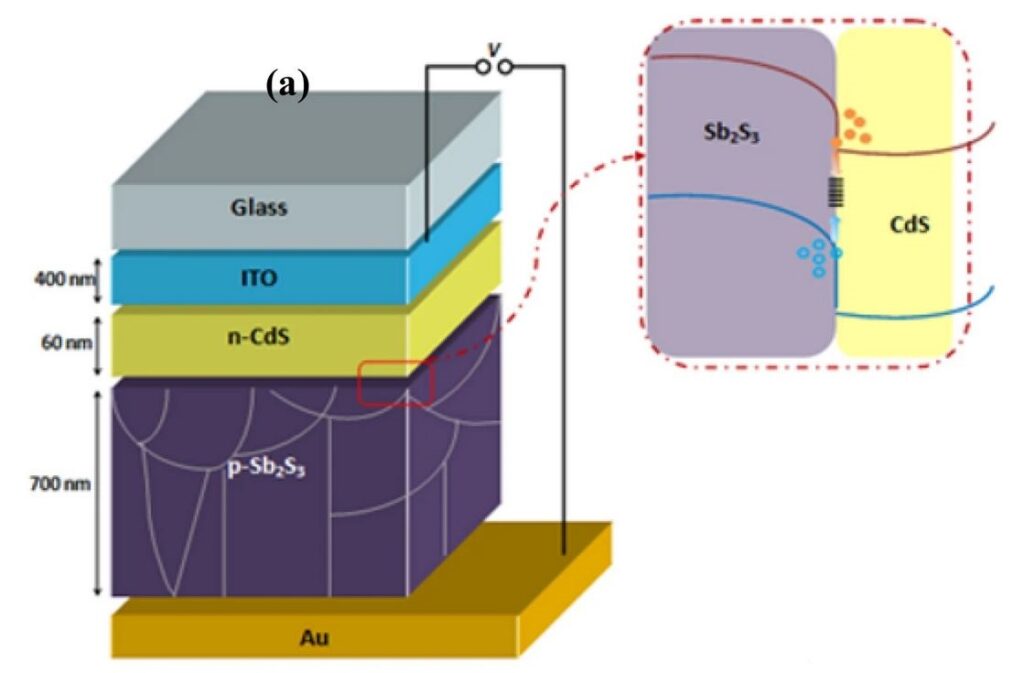
The proposed modeling is utilized to a standard Sb2S3 cell construction combining a substrate with a glass coating of indium tin oxide (ITO), a layer of CdS, a Sb2S3 absorber, and a gold (Au) metallic contact. This evaluation exhibits that rising the doping and thickness of CdS improves the era and separation mechanisms by rising the electrical subject and absorption price.
“The optimized photo voltaic cell configuration exhibits important enhancements with a excessive short-circuit present density of 9.5 mA cm-2an open-circuit voltage of 1.16 V, a fill issue of 54.7%, and a outstanding 30% enhance in conversion effectivity in comparison with typical photo voltaic cells,” stated the scientists, including that the proposed design of the cell can obtain an effectivity of 11.68%, in comparison with 6.5% for a non-optimized machine.
“The simulated work not solely sheds mild on present limitations and prospects but in addition lays the inspiration for future analysis instructions,” the group concluded.
The new cell structure was launched within the research “Investigation of transport phenomena and recombination mechanisms in skinny movie Sb2S3 photo voltaic cell,” revealed in scientific reviews. The analysis group consists of scientists from Algeria’s Laboratory HNS-RE2SD, the Universidad Autónoma de Querétaro in Mexico, the Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences in India and Chettinad Academy of Research and Education, in addition to from King Saud University in Saudi Arabia and Yeungnam University in South Korea.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
[ad_2]
Source link