[ad_1]
US scientists have developed a thermophovoltaic cell that may be paired with low cost thermal storage to offer energy on demand. An indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) thermophovoltaic cell absorbs a lot of the in-band radiation to generate electrical energy, whereas serving as an nearly good mirror.
Thermophotovoltaics (TPV) is an influence technology expertise that makes use of thermal radiation to generate electrical energy in photovoltaic cells. The TPV system typically consists of a thermal emitter that may attain excessive temperatures, near or past 1,000 C, and a photovoltaic diode cell that may take in photons coming from the warmth supply.
The expertise has attracted the curiosity of scientists for many years, as a result of it may capturing daylight throughout all the photo voltaic spectrum and has the technical potential to beat the Shockley-Queisser restrict of conventional photovoltaics. However, the efficiencies reported to date are too low to make them commercially viable, as TPV gadgets nonetheless endure from optical and thermal losses.
With this in thoughts, a gaggle of researchers on the University of Michigan within the United States developed TPV cells reportedly tackle these points and obtain an influence conversion effectivity of 44%.
“This degree of effectivity permits thermal battery methods to achieve a worth level crucial to place a lot of the grid on wind and solar energy,” mentioned the lead creator of the analysis, Andrej Lenert, talking pv journal. “Such methods should proceed to extract power from a scorching storage materials equivalent to graphite because it cools from its most allowable temperature. Obtaining 40% effectivity at storage temperatures of as little as 1300 C, in comparison with the necessity for 2000 C as earlier than, which means that these batteries can get twice as a lot power per kilogram of graphite.
According to Lenert, this consequence represents a serious enchancment in TPVs and solid-state heat-to-power technology usually. “This is a fruits of a few years of intense analysis to learn the way to cut back power loss and mechanical points in TPV air bridge cells, which we initially reported in 2020,” added he. “Those cells have been 32% environment friendly and comparatively weak, now we’re near 44% and with a extra highly effective expertise. Although not but on the kW or MW scale, this consequence exhibits what is feasible with a junction that TPV cells, fulfilling decades-old theoretical predictions made by the TPV group.
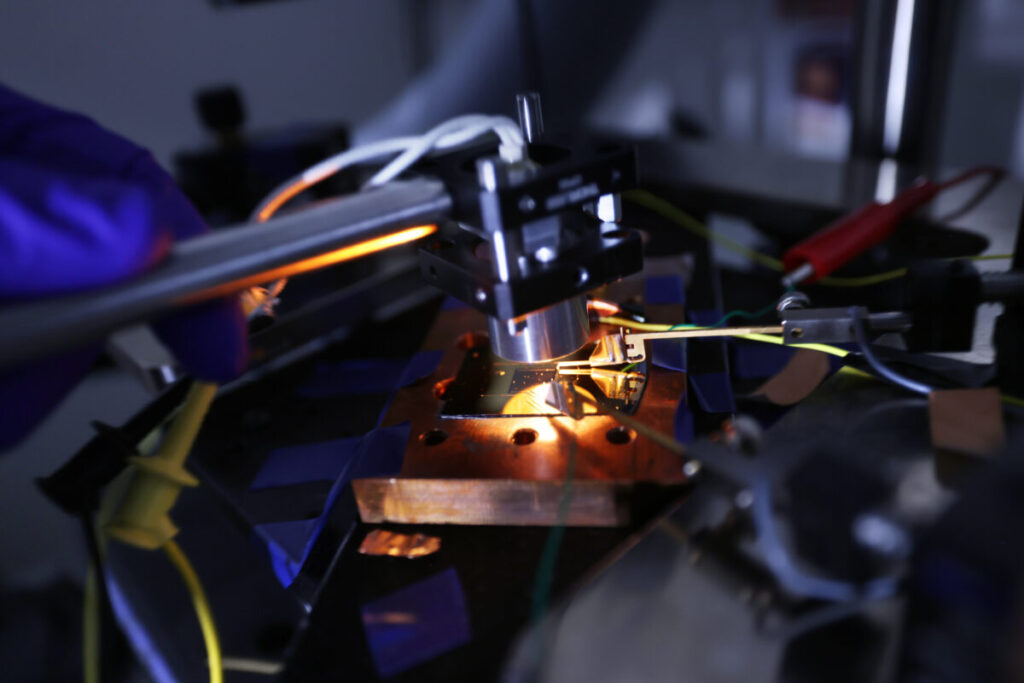
To research “High-efficiency air-bridge thermophotovoltaic cells,” which was not too long ago revealed in Joule, Lenert and his colleagues described the cell as an air-bridge indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) system that may take in a lot of the in-band radiation to generate electrical energy. It can be a virtually good mirror, with almost 99% reflectance.
The cell is constructed utilizing a silicon substrate, an air bridge construction with a thickness of 570 nm, a again contact fabricated from gold (Au), titanium (Ti), an n-doped . InGaAs layer, a membrane layer with a thickness of 1 µm, an InGaAs absorber, and a entrance contact fabricated from Au, Ti, platinum (Pt), and p-doped InGaAs. Three totally different absorber layers have been examined with power bandgaps of 0.74 eV, 0.90 eV, and 1.1 eV, respectively.
the An air-bridge layer is included between the three lively layers and the bottom Au mirror to boost the bottom reflectance and restoration of out-of-band photons. The membrane help layer is meant to attenuate buckling of the free-standing semiconductor membrane and guarantee a single-mode cavity inside the air layer.
“The mixture of a nanoscale air layer and a comparatively excessive protection of the conductive rear electrodes ensures that the air-bridge thermal resistance is small in comparison with that of the Si substrate,” the scientists emphasised. “Additionally, the design features a membrane help layer to attenuate buckling of the free-standing semiconductor membrane and guarantee a single-mode cavity inside the air layer.”
The researchers discovered that the cell with an absorber bandgap of 0.90 eV achieves the most effective efficiency. It achieves an influence conversion effectivity of 43.8% at 1,435 C. “This exceeds the 37% achieved by earlier designs inside this temperature vary,” mentioned Lenert. “We should not but on the effectivity restrict of this expertise. I’m assured that we are going to get increased than 44% and push to 50% within the not too distant future,” added analysis co-author, Stephen R. Forrest.
These outcomes, in keeping with the analysis crew, additionally promise vital enhancements within the round-trip effectivity of the system. “It’s a type of battery, however one which’s not lively. You do not should mine the lithium such as you do with electrochemical cells, which suggests you do not have to compete within the electrical automobile market,” added Forrest. “Unlike pumped water for hydroelectric power storage, you may put it wherever and you do not want a water supply close by.”
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
[ad_2]
Source link