[ad_1]
New analysis from Germany and the USA analyzes the affect of warmth pump (HP) integration on the flexibility of day-ahead load forecasting in vitality communities. Using totally different fashions, the scientists additionally investigated whether or not the HP hundreds must be predicted individually from the remainder of the family or each collectively.
An worldwide analysis group investigated the affect of warmth pumps on neighborhood vitality load forecasting and located that the usage of so-called transformer fashions improves the standard of forecasting.
“Traditional load patterns will change in lots of nations by altering the heating sector to warmth pumps,” the teachers defined. “This growth has a severe affect on operators of vitality communities. First, it’s not clear whether or not the identical forecasting strategies work properly for conventional family hundreds and warmth pump hundreds. Second , the potential affect of the extent of aggregation on neighborhood vitality load forecasts has not been explored.
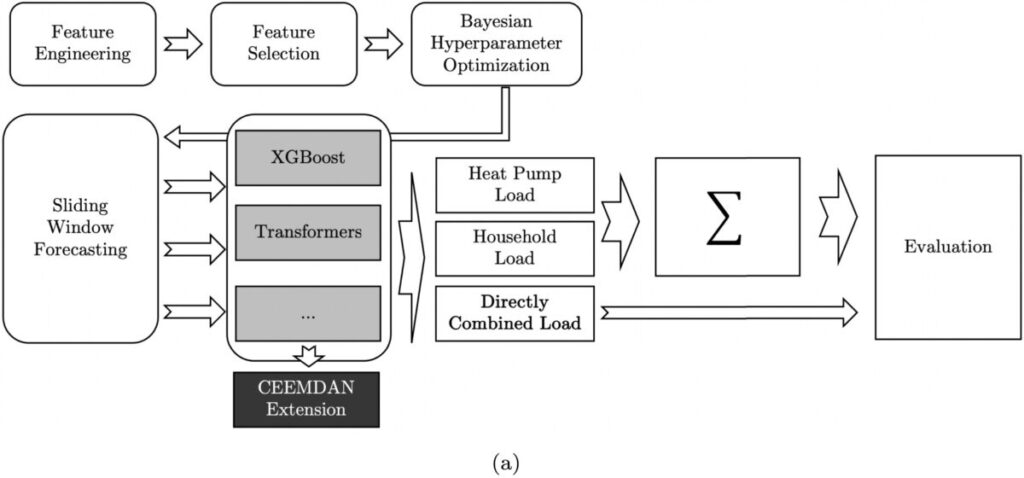
The group makes use of prediction fashions based mostly on machine studying strategies, akin to random forests and XGBoost, in addition to the recurrent neural community strategy of long-short-term reminiscence networks (LSTMs). In addition, it explores the novel neural community structure of transformers.
In addition to the given load and excellent foresight climate information, lecturers recommend extra options which will must be carried out in every forecasting: the kind of solar, cyclical calendric options, the rolling common of obvious temperature, the typical load on the identical time step, and previous hundreds. For every prediction case and prediction methodology, the group used the Bayesian optimization mannequin to establish probably the most related options.
In addition, the researchers used the whole ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (CEEMDAN) methodology as an extension of every forecasting method. “An rising variety of load forecasting research are making use of decomposition strategies to enhance mannequin efficiency,” they defined. “The CEEMDAN algorithm has many benefits over various decomposition strategies: it exhibits a superb dealing with of the mode mixing downside, it’s extra strong to noise, in addition to non-stationarity.”
Image: Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Applied Energy, CC BY 4.0 DEED
All forecasting fashions, extensions, and aggregation eventualities are utilized to a high-quality dataset of family hundreds in an vitality neighborhood in Hamelin, Germany. The dataset contains lively and reactive energy, voltage, and present measurements of 38 households with water-to-water HPs and an extra heating rod as a backup heater. According to the researchers, the set up of HPs, on this case, adjustments the height load from 20.1 kW to 80.1 kW.
The mannequin was educated and analyzed to foretell the hundreds on the low voltage degree of the transformer, the place many households in an vitality neighborhood are linked. Data from 2019 are used for coaching and testing hyperparameter choice, whereas information from 2020 are used for precise benchmarking of various strategies.
The outcomes present that the very best performing forecasting strategies change after the set up of warmth pumps. While random forests or XGBoost present cheap prediction high quality in conventional load forecasting, the transformer-based methodology is extra correct when the information is aggregated by HP.
“The high quality of the forecasting load of the vitality load of the neighborhood every day can’t be elevated by taking separate measurements of the warmth pump hundreds, which might be an extra effort for the vitality neighborhood or operators to distribute the grid,” the outcomes additional present. “Transformer-based fashions additionally present the very best efficiency in a real-world peak discount battery vitality storage system (BESS) use case for the investigated vitality neighborhood with warmth pumps.”
The analysis is offered within the paper “The affect of warmth pumps on the day by day forecasting of the vitality neighborhood load,” printed in Applied Energy.
Researchers from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany and Purdue University in Indiana performed the analysis. “We encourage researchers to make use of our dataset, outcomes, and analysis pipeline, which we publish open-source, to benchmark novel strategies in opposition to them to develop correct prediction strategies for a lot of vitality neighborhood with warmth pumps and apply our methodology to various datasets,” they emphasize.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you need to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
[ad_2]
Source link