[ad_1]
In its newest month-to-month column for pv journal, the IEA-PVPS supplies a complete overview of state-of-the-art practices, finest practices, and proposals for reactive energy administration amid the rising integration of distributed vitality assets (DERs). The article describes regulatory frameworks and sensible functions, highlighting the necessary function of reactive energy administration in sustaining a steady and environment friendly energy grid.
As the worldwide vitality panorama shifts towards renewable vitality sources, efficient administration of reactive energy turns into crucial for guaranteeing grid stability and reliability. The current IEA PVPS Task 14 report, “Reactive Power Management with Distributed Energy Resources,” explores state-of-the-art practices, finest practices, and proposals for managing reactive energy amid rising integration. in distributed vitality assets (DERs). This article supplies a complete overview of the report’s findings, regulatory frameworks, and sensible functions, highlighting the crucial function of reactive energy administration in sustaining a steady and environment friendly energy grid.
The Importance of Reactive Power Management
Reactive energy administration is important for sustaining voltage management, guaranteeing excessive energy high quality, and bettering general grid stability. This helps keep away from points similar to harmonics, flicker, unbalanced hundreds, and energy oscillations, which might negatively have an effect on energy high quality and the power to switch energy successfully. With the rising integration of DERs similar to photovoltaic (PV) programs, these assets should assume larger duty for offering reactive energy management. This enchancment in energy system stability is important for stopping issues similar to load shedding and system collapse, which in the end improves the safety and reliability of the ability system.
Objectives and Objectives of the Report
The IEA PVPS Task 14 report goals to supply a abstract of state-of-the-art administration practices, finest practices, and proposals for reactive energy administration. It examines the regulatory frameworks of chosen nations, highlighting totally different approaches to reactive energy administration. The report affords insights into the present state and future prospects of reactive energy administration within the context of accelerating DER integration and investigates the effectiveness of varied regulatory frameworks in supporting reactive energy administration.
Regulatory Requirements and Practices
The report covers the regulatory necessities of chosen Task 14 nations and examples of analysis and functions from these nations. It supplies an outline of reactive energy rules in several nations, detailing the grid codes and frameworks that form the necessities for linked DERs to supply reactive energy management. . Task 14 examines how these rules affect the operation of energy programs with the rising integration of renewable vitality sources. As an instance of regulatory necessities, Germany might be mentioned on this article.
Example: Germany’s Grid Codes for DER Reactive Power Provision
In Germany, present grid codes mandate that DERs should present managed reactive energy throughout feed-in. The pointers be sure that DERs successfully contribute to grid stability by offering the required reactive energy. This functionality permits Distribution System Operators (DSOs) to make use of DER for added system companies. Requirements fluctuate primarily based on voltage degree:
- Low Voltage (LV): VDE-AR-N 4105 specifies that DERs with a capability of ≤4.6 kVA should present reactive energy with a minimal energy issue of 0.95, whereas bigger DERs should present a minimal energy issue of 0.9.
- Medium Voltage (MV): VDE-AR-N 4110 requires the DER to keep up the reactive energy inside a hard and fast vary if the lively energy feed-in exceeds 20% of the put in capability, guaranteeing the soundness of the widespread level coupling (PCC).
- High Voltage (HV): VDE-AR-N 4120 affords three choices for reactive energy provision primarily based on lively energy feed-in and generator capability. Each variant specifies totally different overexcited and underexcited energy components, permitting DSOs to decide on the most suitable choice for his or her particular wants. DSOs can select one of many proposed choices primarily based on the precise circumstances of every generator’s PCC. HV and additional excessive voltage (EHV) degree turbines should present reactive energy inside one of many fastened reactive energy ranges if their lively energy feed-in exceeds 20% of their whole put in capability.
A standard attribute is that there are little or no reactive energy necessities when feeding little lively energy. The numerous requested reactive energy capabilities are summarized in Figure 1.
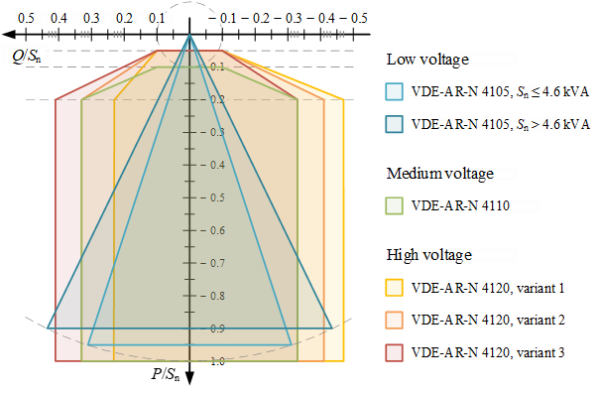
Image: IEA-PVPS
Selected Case Studies
In Germany, the case research focuses on predicting the flexibleness potential of reactive energy in medium-voltage (MV) PV crops. The research examines totally different PV forecasting strategies and introduces a reliability indicator to evaluate the accuracy of reactive energy short-term forecasts. It emphasizes the necessity for top reliability of forecasts to keep away from overestimation and examines using a reactive reserve in energy planning to enhance forecast reliability. This particularly corresponds to intervals of low lively energy infeeds as talked about within the earlier part and highlights the significance of repeatedly updating the grid codes as proven within the Task 14 PV ancillary companies report.
Japan’s method entails evaluating voltage management efficiency underneath totally different eventualities, bearing in mind elevated PV penetration. The research, carried out by a consortium involving TEPCO Power Grid and Waseda University, supported by NEDO, examines voltage management underneath fastened energy issue management. The findings led to a brand new grid code in 2023, which stipulates that energy issue settings should be tailored primarily based on DSO requests, highlighting the necessity for versatile management methods.
The Austrian research targeted on the effectiveness of future measures associated to the community of low-voltage grids. It examines totally different eventualities, together with the influence of local weather insurance policies, regional expertise launches, and totally different operational methods associated to PV, warmth pumps, and e-mobility. The research recognized challenges similar to the necessity for detailed evaluation of Q(V) management contributions and the dearth of huge grid simulation capabilities, which hinder a complete understanding of the worth of administration of reactive energy in distribution grids.
Key Takeaways from the Report
The predominant authors of the report spotlight three necessary components. First, there’s a want for up to date regulatory frameworks to align with the evolving vitality panorama, guaranteeing the soundness and effectivity of energy programs. Second, the potential of DERs as a supply of reactive energy companies must be additional explored, together with improved integration with photo voltaic PV forecasting. Third, collaboration between Transmission System Operators (TSOs) and DSOs is important for efficient reactive energy administration, which might be enhanced by Information and Communications Technology (ICT).
Conclusion of Task 14 and Future Directions
Task 14 ended after 14 years of profitable analysis and improvement within the discipline of PV integration and reactive energy administration. Throughout its three phases, Task 14 has made important strides in addressing technical challenges, creating requirements, and selling finest practices for top penetration of PV programs in energy grids. . With the tip of Task 14, its legacy continues to affect grid administration and renewable integration methods.
Looking forward, Task 19 will start in 2025 as a follow-up to Task 14, constructing on its achievements and persevering with the mission of bettering grid stability and effectivity with extra renewable vitality integration. Task 19 will give attention to managing grids with 100% renewable vitality sources, integrating photo voltaic PV with wind, and defining the function of photo voltaic PV within the sensible grid.
Please discover extra info in IEA PVPS Task 14 and all their publications HERE.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are these of the writer, and don’t essentially replicate these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
Popular content material

[ad_2]
Source link



