[ad_1]
A European analysis staff is investigating interconnection and encapsulation methods to enhance damp warmth and mechanical resilience in car built-in photovoltaic (VIPV) modules, discovering carbon-fibre strengthened plastics to be promising.
To lengthen the driving vary of electrical autos, analysis teams are taking a look at integrating photo voltaic cells into the car’s roof, hood, trunk and physique facet panels. But such automotive photovoltaic (VIPV) functions require new lighter weight modules based mostly on a deep understanding of potential failure mechanisms, and sturdy designs. within the module.
A European analysis staff has reported some progress towards that aim after investigating interconnection and encapsulation methods to enhance VIPV module reliability towards moist warmth and mechanical results.
“In the event of light-weight PV modules with excessive reliability, the mechanical properties of the bill-of-materials used have been discovered to be necessary. We investigated completely different compositions and located the plastics strengthened of carbon-fiber is promising,” the corresponding creator of the analysis, Bin Luo, stated. pv journal. “The most difficult facet is knowing the completely different degradation/failure mechanisms when completely different supplies are used.”
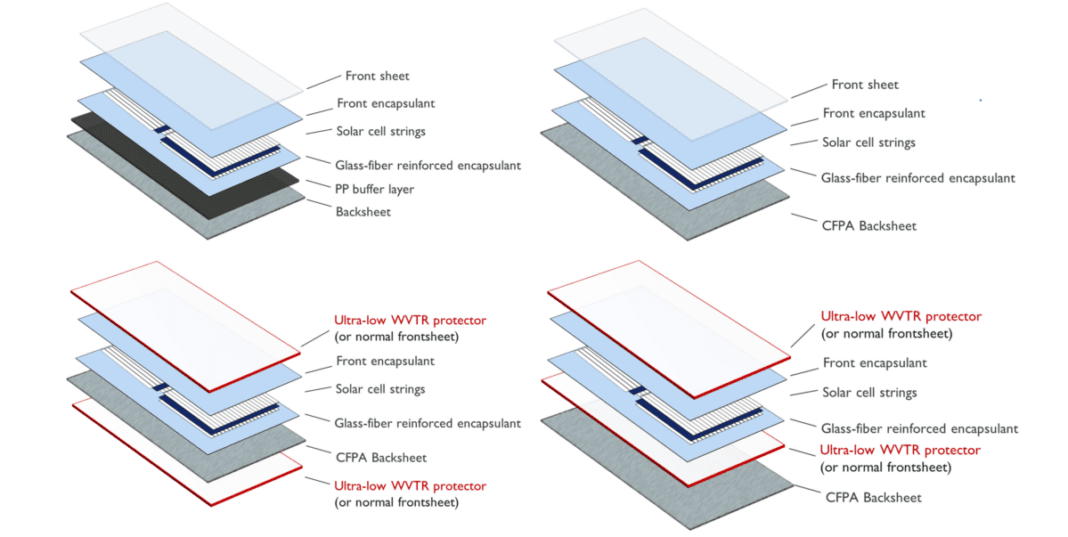
The staff created light-weight mini modules, weighing about 3.45 kg / m2. The backsheets chosen are strengthened with glass-fiber polypropylene or carbon-fiber polypropylene. The again encapsulant is fabricated from polyolefin elastomer (POE) strengthened with randomly oriented brief glass fibers at 8.2% weight ratio. Multi-wire linked heterojunction cell strings, a thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) contact foil, a entrance encapsulant fabricated from polyolefin elastomer (POE), and a polyethylene terephthalate entrance sheet full the construction of the units.
The staff then performed damp warmth and mechanical affect exams, which revealed failures, comparable to cracks within the photo voltaic cell, module delamination, and microcracks within the backsheet. It was then analyzed to reach at a brand new invoice of supplies that included fiber reinforcement within the backsheet and a thicker entrance encapsulant movie.
Using a backsheet with increased bending stiffness reduces international bending, which reduces shear stress and, due to this fact, prevents cell cracks, the staff defined. As for damp warmth resistance, which is dependent upon the water vapor permeability of the supplies within the module stack, the staff addressed it from the entrance and the again.
The result’s a design that features a carbon-fiber polyamide backsheet and new low-moisture transmission layers within the module. The design selections elevated the burden to five.21 kg/m2 and elevated the fee, however the technique enabled extra stability within the beforehand noticed failure modes.
In the dialogue about utilizing non-traditional supplies to offer safety and reliability to the module, the staff was conscious of the trade-offs between weight and price. “Further testing and price optimization is required to deliver it to commercialization,” Luo stated.
The examine is described in “Encapsulation methods for mechanical affect and damp warmth reliability enchancment in light-weight photovoltaic modules towards vehicle-integrated functions,” revealed in Solar power supplies and photo voltaic cells. Researchers from KU Leuven in Belgium, IMEC, Hasselt University, and EnergyVille, in addition to Switzerland’s Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), and the Austrian Research Institute for Chemistry and Technology.
Looking forward to future analysis subjects, the staff sees a necessity for built-in reliability exams, together with hail affect, thermal biking, and damp warmth exams, together with an evaluation of statistics. Further testing of curved light-weight PV modules on a bigger scale can be required.
Luo broadened the long run perspective of the analysis when he stated, “We wish to construct extra on our understanding of the failure mechanisms of varied light-weight PV buildings and the hyperlink to the fabric properties beneath the completely different stress circumstances associated to PV on the whole but additionally particularly for various built-in PV functions.”
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link